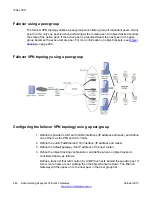
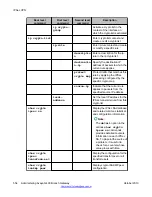
Failover using a peer-group
The failover VPN topology utilizes a peer-group which lists a group of redundant peers. At any
point in time, only one peer is active and acting as the remote peer. An object tracker monitors
the state of the active peer. If the active peer is presumed dead, the next peer in the peer-
group becomes the active remote peer. For more information on object trackers, see
on page 282.
Failover VPN topology using a peer-group
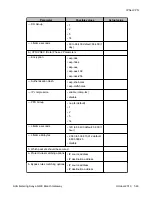
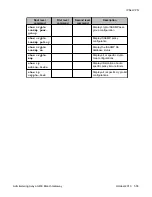
Configuring the failover VPN topology using a peer-group
1. Define the private VLAN1 and VLAN2 interfaces (IP address and mask), and define
one of them as the PMI and ICC-VLAN.
2. Define the public FastEthernet 10/3 interface (IP address and mask).
3. Define the default gateway (the IP address of the next router).
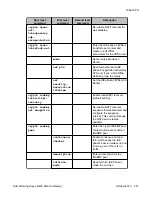
4. Define the object tracking configuration, and define when an object tracker is
considered down, as follows:
Define a track list that will monitor (by ICMP) five hosts behind the specific peer. If
two or more hosts are not working then the object tracker is down. The Branch
Gateway will then pass on to the next peer in the peer group list.
IPSec VPN
542 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway
October 2013
Summary of Contents for G430
Page 1: ...Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway Release 6 3 03 603228 Issue 5 October 2013 ...
Page 12: ...12 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 ...
Page 246: ...VoIP QoS 246 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Page 556: ...IPSec VPN 556 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...