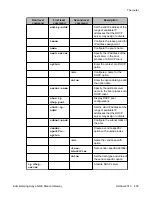
Configuring a distribution access list example
on page 465
on page 465
on page 466
RIPv1
RIPv1 is the original version of the RIP protocol. The RIPv1 protocol imposes some limitations
on the network design with regard to subnetting. When operating RIPv1, you must not configure
variable length subnetwork masks (VLMS). Each IP network must have a single mask, implying
that all subnetworks in a given IP network are of the same size. Also, when operating RIPv1,
you must not configure supernets. RIPv1 is defined in RFC 1058.
RIPv2
RIPv2 is a newer version of the RIP routing protocol. RIPv2 solves some of the problems
associated with RIPv1. The most important change in RIPv2 is the addition of a
subnetwork
mask
field which allows RIPv2 to support variable length subnetworks. RIPv2 also includes
an authentication mechanism similar to the one used in OSPF. RIPv2 is defined in RFC 2453.
For more information, see
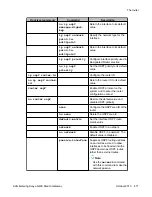
RIPv1 vs. RIPv2
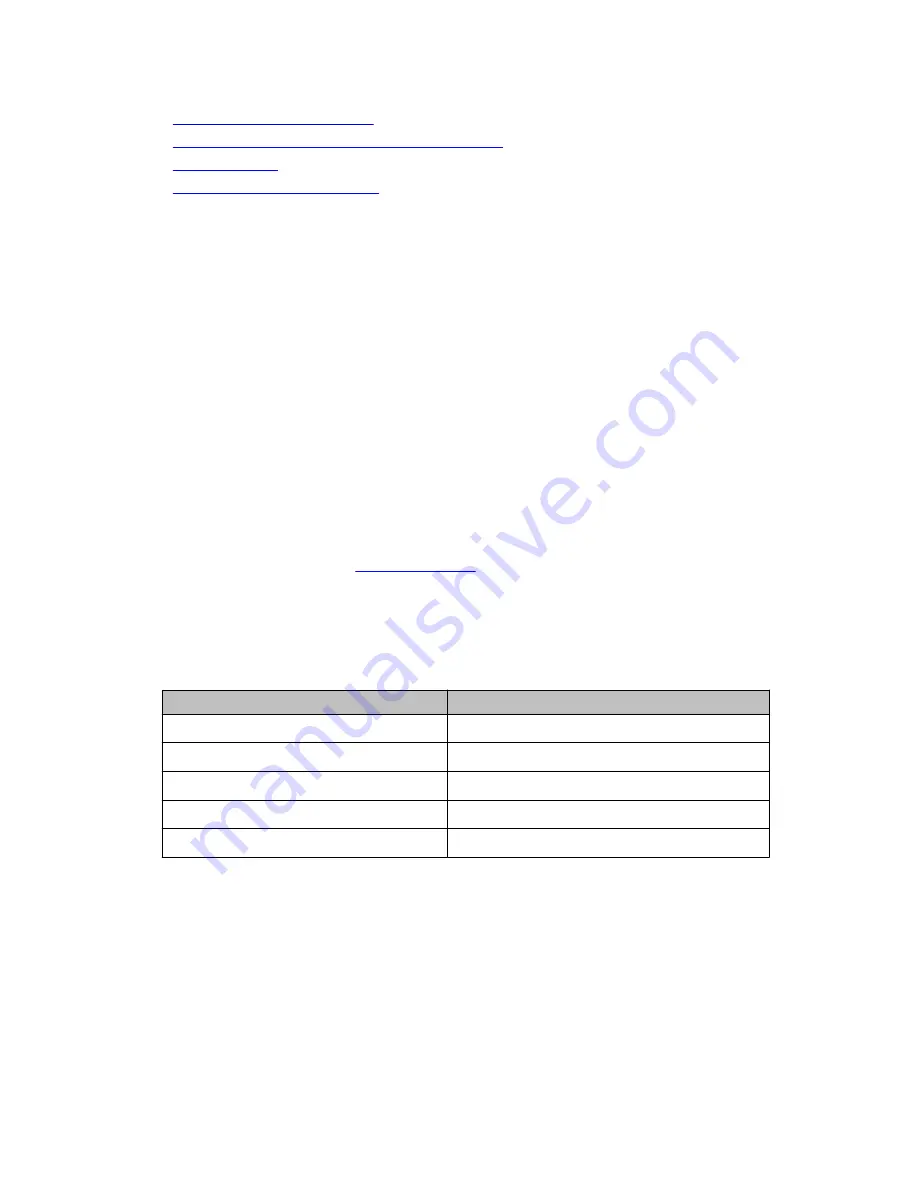
RIPv1
RIPv2
Broadcast addressing
Multicast addressing
Timer-based – updated every 30 seconds Timer-based – updated every 30 seconds
Fixed subnetwork masks
VLSM support – subnet information transmitted
No security
Security (authentication)
No provision for external protocols
Provision for EGP/BGP (Route tag)
The router
Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway
October 2013 463
Summary of Contents for G430
Page 1: ...Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway Release 6 3 03 603228 Issue 5 October 2013 ...
Page 12: ...12 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 ...
Page 246: ...VoIP QoS 246 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Page 556: ...IPSec VPN 556 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...