each virtual router agent to address any network security issues. To disable proxy on an
agent (router), you must use SNMP or the CLI
snmp-server proxy disable
command.
NOTE:
Disabling the proxy function on a particular virtual router disables the
use of proxy through that virtual router. You can, however, use the proxy
function to access a proxy-disabled virtual router through another virtual
router that does have the proxy function enabled.
Communicating with the SNMP Engine
The SNMP engine performs the following tasks for SNMPv3:
•
Sends and receives messages.
•
Prepares messages and extracts data from messages.
•
Authenticates, encrypts, and decrypts messages.
•
Determines whether access to a managed task is allowed.
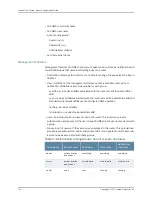
Each SNMP engine has an SnmpEngine ID, a hexadecimal number 15 octets long. Table
18 on page 144 shows the structure of the SnmpEngine ID.
Table 18: SnmpEngineID Structure Object
Description
Octet
Assignment
E Series router SNMP management private enterprise number
1 – 4
Indicates that octets 6–15 contain information determined by the E Series
router
5
The MAC address for the device. For E120 and E320 routers, the MAC
address is a unique ID based on chassis ID.
6 – 11
The 32-bit (4 octet) router index (or routerUID)
12 – 15
Request protocol data units (PDUs) for the SNMP engine must contain the corresponding
contextEngine ID and contextName for the SNMP engine. When the system receives a
PDU, it examines the contextEngine ID and contextName, and forwards the request to
the corresponding virtual router.
•
The contextEngine ID is the same as the SnmpEngine ID.
•
The contextName is an internally derived ASCII string associated with the router. It has
the format
routerN
, where N is a number (with no leading zeros) in the range 1–16777215,
corresponding to the least significant 24 bits of the 32-bit router index (or router UID).
You can obtain the contextName for a specific router through the Juniper-ROUTER-MIB
from the juniRouterContextName object in the juniRouterTable, which is indexed by
the 32-bit router index (juniRouterIndex).
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
144
JunosE 11.3.x System Basics Configuration Guide
Содержание JUNOSE 11.3
Страница 6: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc vi...
Страница 8: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc viii JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Страница 24: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc xxiv JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Страница 32: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 2 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Страница 146: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 116 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Страница 166: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 136 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Страница 432: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 402 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Страница 488: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 458 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Страница 524: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 494 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Страница 554: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 524 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Страница 566: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 536 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Страница 588: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 558 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Страница 613: ...PART 3 Index Index on page 585 583 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc...
Страница 614: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 584 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Страница 632: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 602 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...