5-266
L90 LINE CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEM – INSTRUCTION MANUAL
GROUPED ELEMENTS
CHAPTER 5: SETTINGS
5
To increase security for three phase faults very close to the VTs used to measure the polarizing voltage, a voltage memory
feature is incorporated. This feature stores the polarizing voltage the moment before the voltage collapses, and uses it to
determine direction. The voltage memory remains valid for one second after the voltage has collapsed.
The main component of the phase directional element is the phase angle comparator with two inputs: the operating signal
(phase current) and the polarizing signal (the line voltage, shifted in the leading direction by the characteristic angle, ECA).
The table shows the operating and polarizing signals used for phase directional control.
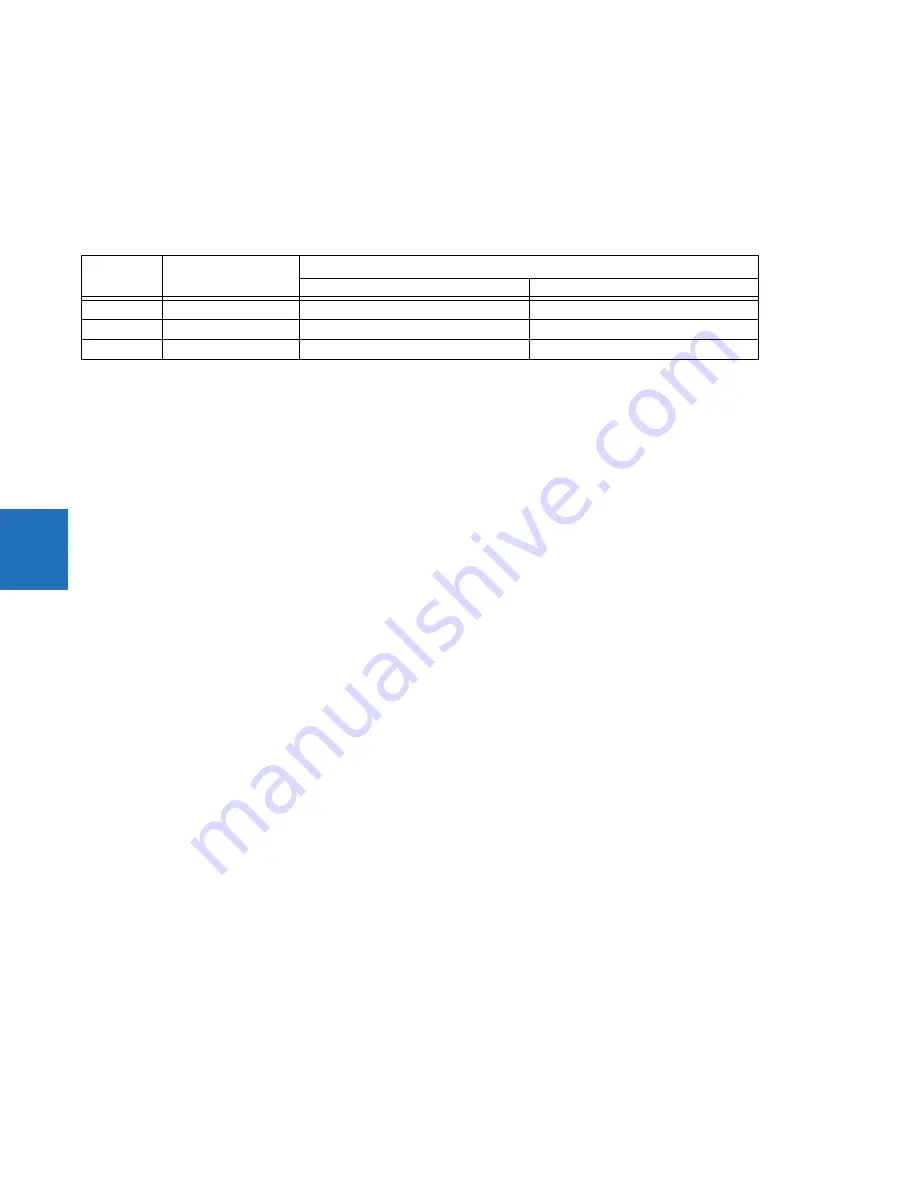
Table 5-36: Operating and polarizing signals
Mode of operation
•
When the function is “Disabled” or the operating current is below 5%
×
CT nominal, the element output is logic “0”
•
When the function is “Enabled,” the operating current is above 5%
×
CT nominal, and the polarizing voltage is above
the
PRODUCT SETUP
DISPLAY PROPERTIES
VOLTAGE CUT-OFF LEVEL
value, the element output is dependent on the
phase angle between the operating and polarizing signals:
–
The element output is logic “0” when the operating current is within polarizing voltage ±90°
–
For all other angles, the element output is logic “1”
•
Once the voltage memory has expired, the phase overcurrent elements under directional control can be set to block or
trip on overcurrent as follows:
–
When
BLOCK WHEN V MEM EXP
is set to “Yes,” the directional element blocks the operation of any phase
overcurrent element under directional control when voltage memory expires
–
When
BLOCK WHEN V MEM EXP
is set to “No,” the directional element allows tripping of phase overcurrent elements
under directional control when voltage memory expires
In all cases, directional blocking is permitted to resume when the polarizing voltage becomes greater than the polarizing
voltage threshold.
Settings
PHASE DIR 1 FUNCTION
— This setting enables and disables the phase directional overcurrent protection element.
PHASE DIR 1 SIGNAL SOURCE
— This setting is used to select the source for the operating and polarizing signals. The
operating current for the phase directional element is the phase current for the selected current source. The polarizing
voltage is the line voltage from the phase VTs, based on the 90° or quadrature connection and shifted in the leading
direction by the element characteristic angle (ECA).
PHASE DIR 1 BLOCK
— Assertion of the operand assigned to this setting blocks operation of the phase directional
overcurrent element.
PHASE DIR 1 ECA
— This setting specifies the element characteristic angle, that is, the angle by which the polarizing voltage
is shifted in the leading direction to achieve dependable operation. In the design of the UR-series elements, a block is
applied to an element by asserting logic 1 at the blocking input. Program the phase directional overcurrent element using
this setting so that the output is logic 1 for current in the non-tripping direction.
PHASE DIR 1 POL V THRESHOLD
— This setting is used to establish the minimum level of voltage for which the phase angle
measurement is reliable. The setting is based on VT accuracy.
PHASE DIR 1 BLOCK WHEN V MEM EXP
— This setting is used to select the required operation upon expiration of voltage
memory. When set to "Yes," the directional element blocks the operation of any phase overcurrent element under
directional control, when voltage memory expires. When set to "No," the directional element allows tripping of phase
overcurrent elements under directional control.
Phase
Operating signal
Polarizing signal V
pol
ABC phase sequence
ACB phase sequence
A
angle of IA
angle of VBC
×
(1
∠
ECA)
angle of VCB
×
(1
∠
ECA)
B
angle of IB
angle of VCA
×
(1
∠
ECA)
angle of VAC
×
(1
∠
ECA)
C
angle of IC
angle of VAB
×
(1
∠
ECA)
angle of VBA
×
(1
∠
ECA)
Содержание L90
Страница 14: ...1 4 L90 LINE CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEM INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR FURTHER ASSISTANCE CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1 ...
Страница 68: ...2 54 L90 LINE CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEM INSTRUCTION MANUAL SPECIFICATIONS CHAPTER 2 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION 2 ...
Страница 136: ...3 68 L90 LINE CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEM INSTRUCTION MANUAL CONNECT TO D400 GATEWAY CHAPTER 3 INSTALLATION 3 ...
Страница 224: ...4 88 L90 LINE CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEM INSTRUCTION MANUAL FLEXLOGIC DESIGN USING ENGINEER CHAPTER 4 INTERFACES 4 ...
Страница 692: ...6 36 L90 LINE CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEM INSTRUCTION MANUAL PRODUCT INFORMATION CHAPTER 6 ACTUAL VALUES 6 ...
Страница 708: ...7 16 L90 LINE CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEM INSTRUCTION MANUAL TARGETS MENU CHAPTER 7 COMMANDS AND TARGETS 7 ...
Страница 742: ...9 6 L90 LINE CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEM INSTRUCTION MANUAL TESTING CHAPTER 9 COMMISSIONING 9 ...
Страница 804: ...10 62 L90 LINE CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEM INSTRUCTION MANUAL FAULT LOCATOR CHAPTER 10 THEORY OF OPERATION 10 ...
Страница 872: ...C 6 L90 LINE CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEM INSTRUCTION MANUAL COMMAND LINE INTERFACE APPENDIX C COMMAND LINE INTERFACE C ...
Страница 878: ...D 6 L90 LINE CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEM INSTRUCTION MANUAL REVISION HISTORY APPENDIX D MISCELLANEOUS D ...
Страница 882: ...iv L90 LINE CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEM INSTRUCTION MANUAL ABBREVIATIONS ...
Страница 900: ...xviii L90 LINE CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL SYSTEM INSTRUCTION MANUAL INDEX ...
















































