ZENER 8000-V Installation Manual
_
24
IM00165
EIA/RS-485 Communications Wiring
The ZENER 8000-V communications port is EIA/RS-485 compliant and is isolated from ground and other circuits.
This communications port is used by BACnet MS/TP and Modbus RTU protocols.
The communications system (communications cable, ZENER 8000-V and other devices) needs to operate reliably
in a potentially electrically noisy environment. For best performance and to reduce the risk of network failure,
we recommend the following:
Best practice
Best practice for EIA/RS-485 communications requires 3 conductors and a shield. It is frequently discussed in
terms of being a two wire network, but this is not the case.
Two conductors are used to carry the EIA/RS-485 data as a differential voltage signal. These wires should ideally
be twisted together so that any magnetically induced interference voltage will occur equally in both conductors
and be rejected by the differential nature of the EIA/RS-485 interface circuit.
The third conductor is used to keep the common connection (marked as terminal “C” in ZENER 8000-V) in all the
communications interfaces at the same potential, that is, keep the common mode voltage at each interface
within the limits specified by the standard.
The Shield is connected to earth/ground at one end
3
only and provides protection against capacitive coupling to
nearby cables and other electrical noise sources.
One arrangement that meets these requirements using generic materials is as follows:
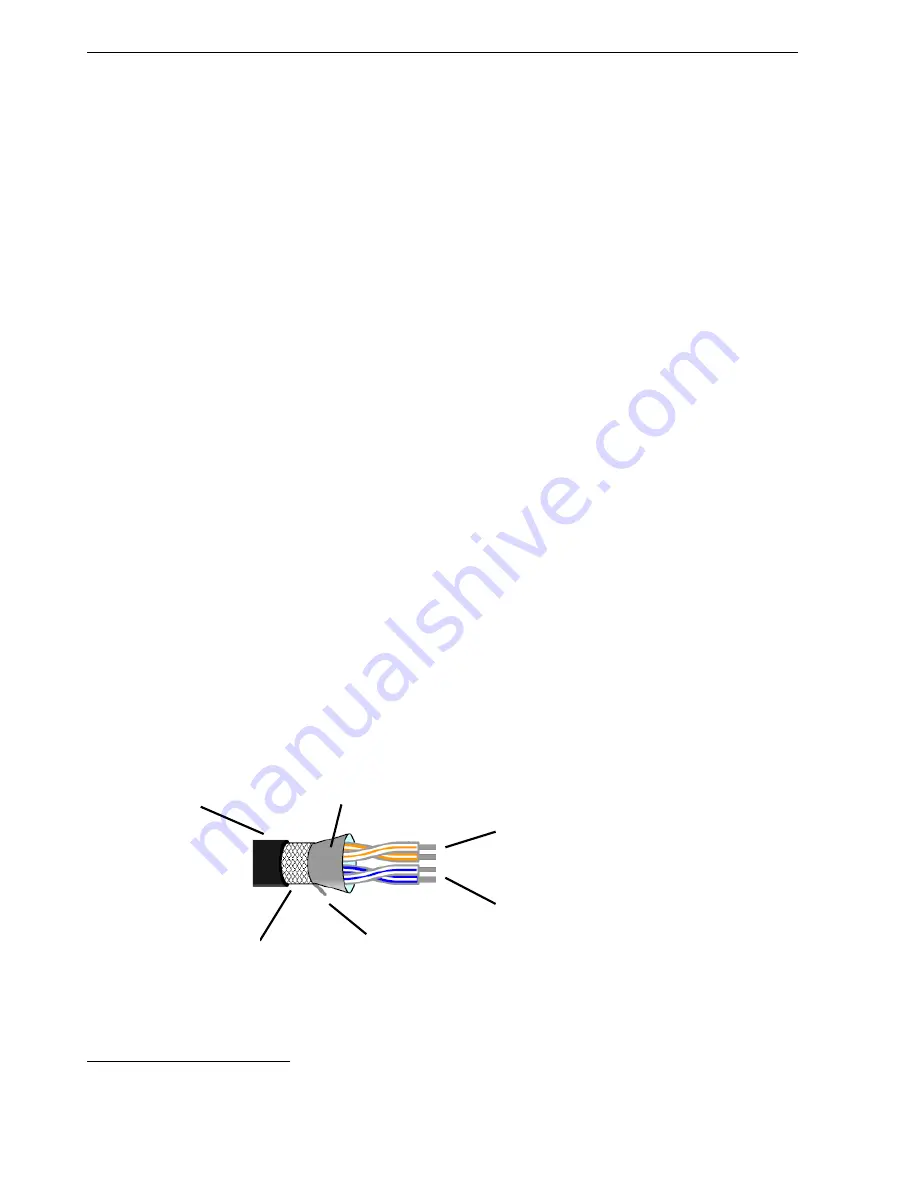
Use a standard two pair shielded instrumentation cable. Internally, this will have a total of 4 conductors,
physically arranged as two twisted pairs surrounded by an aluminium wrapper as a screen. A bare
“drain wire”, in contact with the aluminium wrapper, makes an electrical connection to the screen.
One pair is used for the data signals. The other pair is used in parallel as the common wire. The screen
(drain wire) is connected to ground at one end only.
3
Why one end only? Because there will be voltage differences between various ground points in an electrical installation
that contain significant amounts of electrical noise and occasionally significant power frequency voltages during electrical
fault events. We don’t want these voltages to cause a current in the communications cable screen (because it would then
induce a voltage in the cable conductors inside), so we ground the screen at one point only.
Cable jacket
Use this pair, shorted
together, for the
common (C) connection
Use this pair for the
A & B wires
Foil screen
Drain wire for screen
connection
Some cables may
also have a braided
screen (better, but
more expensive)















































