912
Appendix A: Functions and Instructions
|
(“with”)
Í
key
expression
|
Boolean expression1
[
and Boolean
expression2
]
...
[
and Boolean expressionN
]
The “with” (|) symbol serves as a binary operator.
The operand to the left of | is an expression. The
operand to the right of | specifies one or more
relations that are intended to affect the
simplification of the expression. Multiple relations
after | must be joined by a logical “and”.
The “with” operator provides three basic types of
functionality: substitutions, interval constraints,
and exclusions.
x+1| x=3
¸
4
x+y| x=sin(y)
¸
sin(y)
+
y
x+y| sin(y)=x
¸
x
+
y
Substitutions are in the form of an equality, such
as
x=3
or
y=sin(x)
. To be most effective, the left
side should be a simple variable.
expression
|
variable
=
value
will substitute
value
for every
occurrence of
variable
in
expression
.
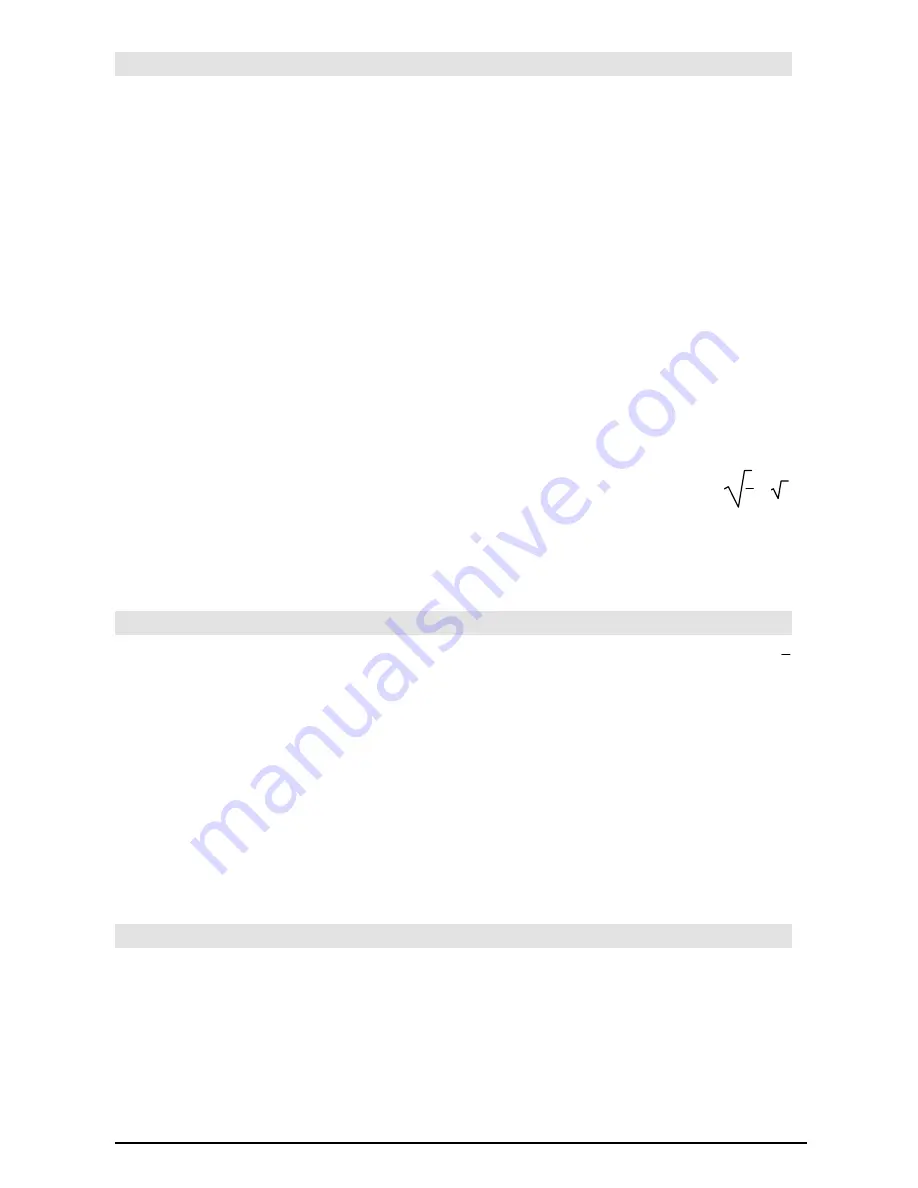
x^3
ì
2x+7
!
f(x)
¸
Done
f(x)| x=
‡
(3)
¸
‡
3
+
7
(sin(x))^2+2sin(x)
ì
6| sin(x)=d
¸
d
ñ
+2d
ì
6
Interval constraints take the form of one or more
inequalities joined by logical “and” operators.
Interval constraints also permit simplification that
otherwise might be invalid or not computable.
solve(x^2
ì
1=0,x)|x>0 and x<2
¸
x
=
1
‡
(x)
ù
‡
(1/x)|x>0
¸
1
‡
(x)
ù
‡
(1/x)
¸
1
x
ø
x
Exclusions use the “not equals” (/= or
ƒ
)
relational operator to exclude a specific value
from consideration. They are used primarily to
exclude an exact solution when using
cSolve()
,
cZeros()
,
fMax()
,
fMin()
,
solve()
,
zeros()
, etc.
solve(x^2
ì
1=0,x)| x
ƒ
1
¸
x
=
ë
1
!
(store)
§
key
expression
!
var
list
!
var
matrix
!
var
expression
!
fun_name(parameter1,...)
list
!
fun_name(parameter1,...)
matrix
!
fun_name(parameter1,...)
If variable
var
does not exist, creates
var
and
initializes it to
expression
,
list
, or
matrix
.
If
var
already exists and if it is not locked or
protected, replaces its contents with
expression
,
list
, or
matrix
.
Hint:
If you plan to do symbolic computations
using undefined variables, avoid storing anything
into commonly used, one-letter variables such as
a, b, c, x, y, z, etc.
p
/4
!
myvar
¸
p
4
2cos(x)
!
Y1(x)
¸
Done
{1,2,3,4}
!
Lst5
¸
{1 2 3 4}
[1,2,3;4,5,6]
!
MatG
¸
[
1 2 3
4 5 6
]
"Hello"
!
str1
¸
"Hello"
¦
(comment)
Program Editor/Control menu
or
¥
d
key
¦
[
text
]
¦
processes
text
as a comment line, which can be
used to annotate program instructions.
¦
can be at the beginning or anywhere in the
line. Everything to the right of
¦
, to the end of
the line, is the comment.
Program segment:
©
:
¦
Get 10 points from the Graph
screen
:For i,1,10
¦
This loops 10 times
©
Summary of Contents for TI-89 Voyage 200
Page 1: ...TI 89 Titanium Graphing Calculator...
Page 35: ...Getting Started 35 2 B u s i n e s s D B D B Press Result...
Page 44: ...Getting Started 44 3 0 D B D D Press Result...
Page 45: ...Getting Started 45 B D D 2 0 0 2 Press Result...
Page 46: ...Getting Started 46 D B Scroll down to October and press D 1 9 Press Result...
Page 60: ...Getting Started 60 Example Set split screen mode to TOP BOTTOM Press Result 3 B D...
Page 63: ...Getting Started 63 2 D B 4 Press Result...
Page 453: ...Differential Equation Graphing 453...
Page 468: ...Tables 468...
Page 539: ...Data Matrix Editor 539...
















































