An Overview of the Inverter
2-3
605C Frequency Inverter
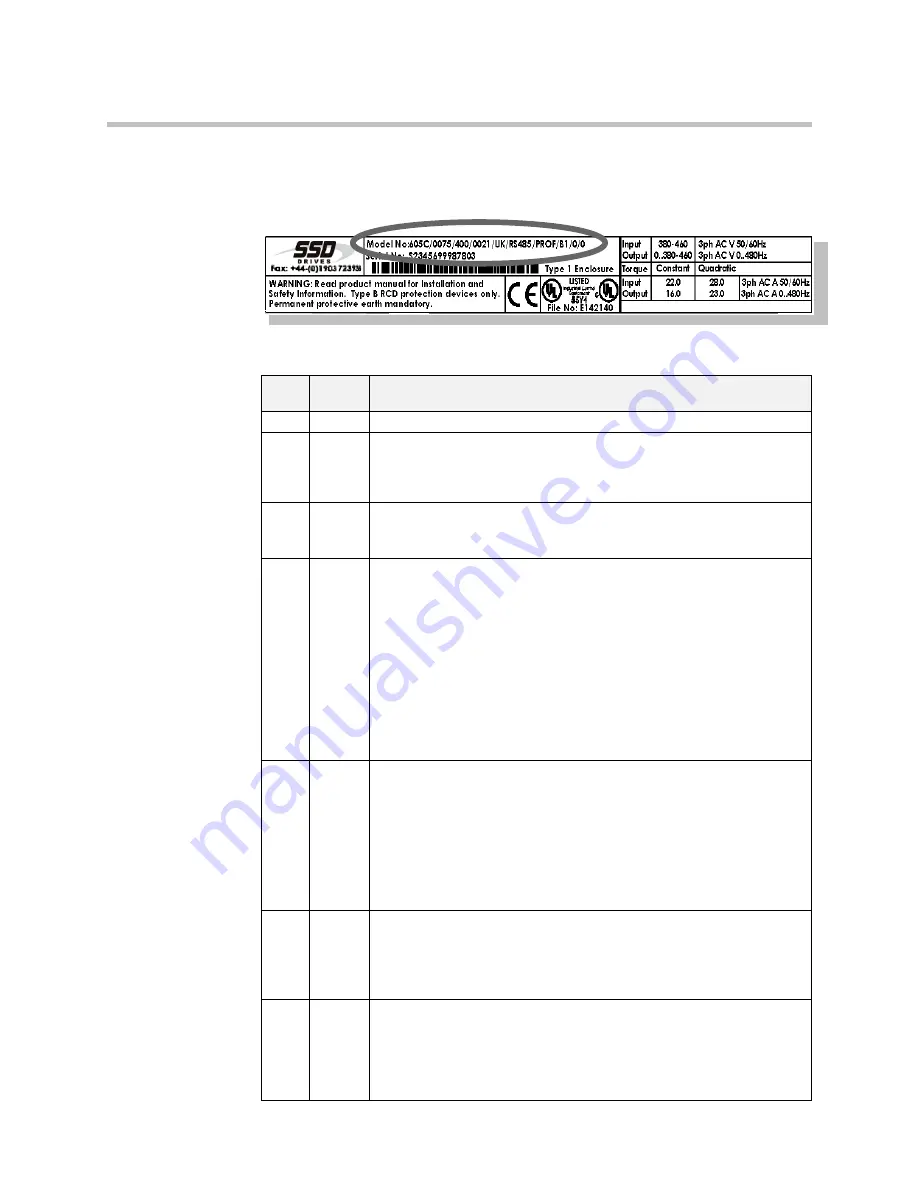
Understanding the Product Code
The 605C unit is fully identified using a ten block alphanumeric code which records how the
Inverter was calibrated, and its various settings when despatched from the factory.
The Product Code appears as the “Model No.”. Each block of the Product Code is identified as
below:
Note:
The Language field controls the default setting for the
BASE FREQUENCY
parameter.
Block
No.
Variable Description
1
605C
Generic product
2
XXXX
Four numbers specifying the power output, for example:
0055 = 5.5kW
0075 = 7.5kW
0110 = 11kW
3
XXX
Three numbers specifying the nominal input voltage rating:
400
380 to 460V (
±
10%) 50/60Hz
500 500V
(
±
10%) 50/60Hz
4
XXXX
Four digits specifying the mechanical package including livery and
mechanical package style:
First two digits
Livery
00
Standard SSD Drives livery
01-99
Defined customer liveries
Third digit
Mechanical packaging style
1
Standard (IP20), protected panel mounting
2
IP20 and falling dirt protection (UL Type 1) wall mounting
Fourth digit
Operator Station
0
No Operator Station
1
6051 Operator Station option fitted
5
XX
Two characters specifying the user interface language.
These characters are the same as used for computer keyboard specifications:
UK
English (50Hz)
US
United States (E 60Hz)
GR
German (50Hz)
FR
French (50Hz)
SP
Spanish (50Hz)
P5
P Language (50Hz)
P6
P Language (60Hz)
6
XXX
Three characters specifying the speed feedback option, 6054 (Technology
Option 1), installed over and above the standard features of the product:
0
No additional option fitted
RS422 Wire ended encoder feedback RS422
HTTL
Wire ended encoder feedback HTTL
7
XXXX
Four characters specifying the communications option protocol, 6055
(Technology Option 2), and its hardware implementation method:
0
No technology option fitted
EI00
EI ASCII/Bisync with hardware implementation 1 (RS485/422)
PROF
Profibus protocol
LINK
LINK protocol
Summary of Contents for 605C
Page 16: ...1 4 Getting Started 605C Frequency Inverter ...
Page 22: ...2 6 An Overview of the Inverter 605C Frequency Inverter ...
Page 50: ...4 14 Operating the Inverter 605C Frequency Inverter ...
Page 66: ...5 16 The Operator Station 605C Frequency Inverter ...
Page 156: ...8 2 Routine Maintenance and Repair 605C Frequency Inverter ...
Page 184: ...10 22 Parameter Specification 605C Frequency Inverter ...
Page 212: ...13 6 Application Notes 605C Frequency Inverter ...
Page 214: ...14 2 Serial Communications 605C Frequency Inverter ...
Page 236: ......
















































