Buried cable applications
Page 42
FiberPatrol FP1150 Product Guide
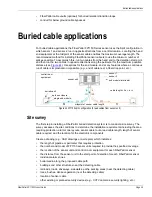
Sensor cable bypasses
In some instances, it may be necessary to bypass an area along the cable path and then continue
the detection beyond the bypass. A typical situation like this occurs when the cable crosses a road
(see
Figure 48
) or if a pipeline must go above ground to get past a river. In either case, the
detection is disabled in software for the section of cable that must be bypassed. For a road
crossing, the sensor cable may require protection by conduit that is sealed at both ends. For
pipeline protection, when the sensor cable goes above ground, it is strapped to the pipe at 1 to 2 m
intervals.
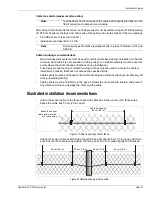
Figure 49
illustrates the method for above ground sensor cable bypasses.
Cable requirements
Calculating the total length of fiber optic cable is one of the most critical phases of site planning.
Other equipment requirements, including the necessary software activation license, are
determined by the length of cable:
Figure 48 Sensor cable bypass (road crossing)
Figure 49 Sensor cable bypass (body of water)
Note
Each FP1150 SU supports up to 500 m of lead cable that does not
count against the per meter software activation license.
software bypass
conduit sealed at both ends
conduit
detection ends
at bypass
detection continues
past bypass
pipeline
detection ends
sensor cable
above ground
detection continues
below ground
wire ties
body of water