Using the built-in Ethernet sniffer
148
SmartWare Software Configuration Guide
12 • Ethernet port configuration
The following is an example of how the sniffer is normally used:
Note
It is possible to capture packets on multiple Ethernet ports at the same time.
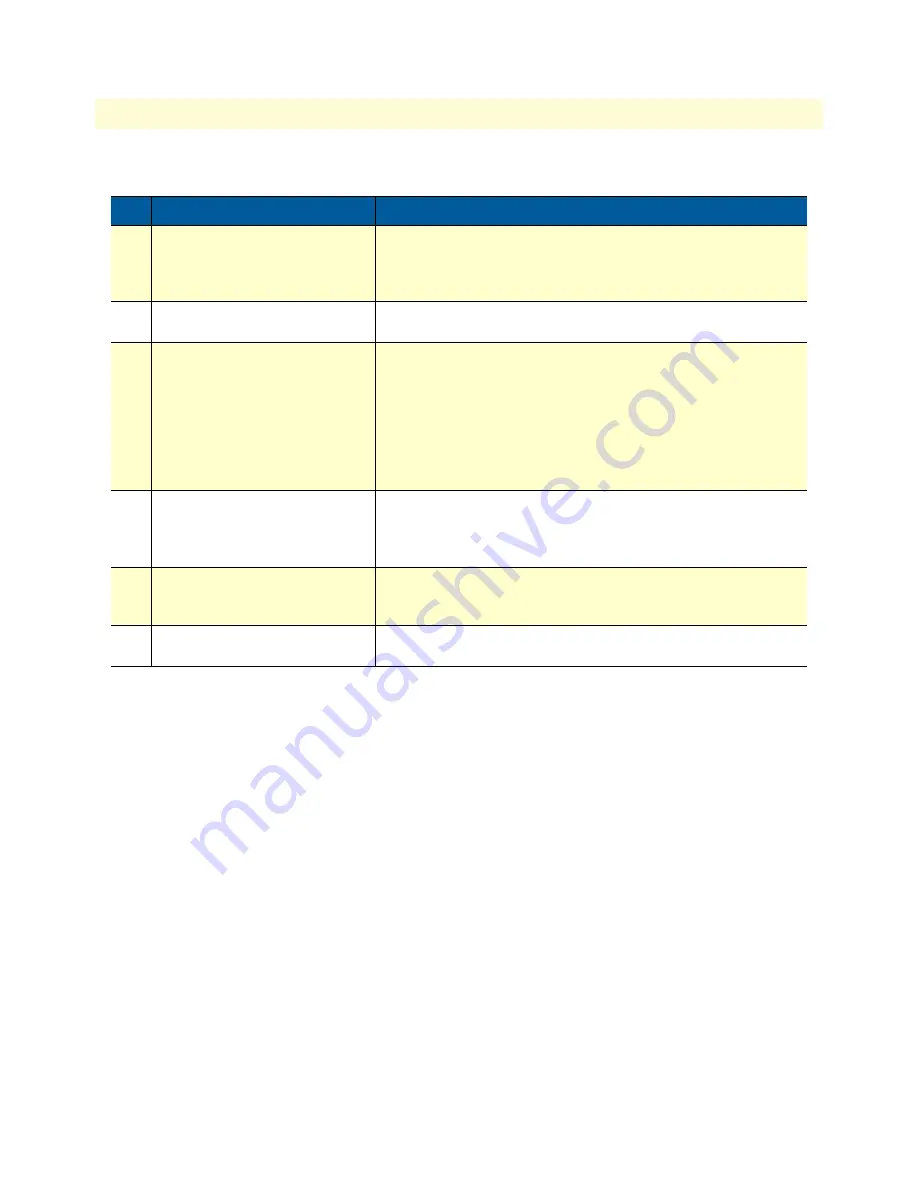
Step
Command
Purpose
1
[
name
] (cfg)# sniff ethernet
0 1 [wrap]
Enable the sniffer on ethernet port 0 1. (Normally the sniffer stops
capturing, if the capture buffer is full. However, if the ‘wrap’ option is
specified, the sniffer starts discarding the oldest packets and retains
the newest ones, if the capture buffer is full.)
2
Now the sniffer is active and will capture the datapackets on the
specified ethernet port.
3
[
name
] (cfg)# no sniff ether-
net 0 1]
Disable the sniffer on ethernet port 0 1. (Note, that the captured
data is not stored to flash memory unless you issue this command)
The file in the flash memory will be named as follows:
nvram:ethernet-0-<slot>-<port>.cap
In this example the name will be:
nvram:ethernet-0-0-1.cap
4
[
name
] (cfg)# copy
nvram:ethernet-0-0-1.cap
tftp://tftp.mypc.net/
capture.cap
Copy the capture file via TFTP to a workstation.
5
[
name
] (cfg)# erase
nvram:ethernet-0-0-1.cap
Erase the capture file on the system to save flash memory.
6
Now the capture file capture.cap can be viewed on a workstation
with Ethereal for example.















































