3-26
j
Position Loop Gain
Adjust the position loop gain according to the rigidity of the machine.
The responsiveness of the servo system is determined by the position loop gain. When a servo system
has high position loop gain, the responsiveness is greater and positioning can be faster. In order for
position loop gain to be raised, the mechanical rigidity and the characteristic frequency must be in-
creased. For general NC machine tools, the range is 50 to 70 (1/s); for general machinery and assembly
devices, it is 30 to 50 (1/s); for industrial robots, it is 10 to 30 (1/s).
The factory setting for position loop gain is 40 (1/s), so it should be lowered for systems with low rigidity.
If a system has low rigidity or low characteristic frequency, increasing the position loop gain sympathetic
vibration of machinery will occur and an alarm will be generated.
Position loop gain is generally expressed as follows:
Position loop gain (Kp) =
Instruction command frequency (pulses/s)
Deviation counter’s residual pulse amount (pulses)
(1/s)
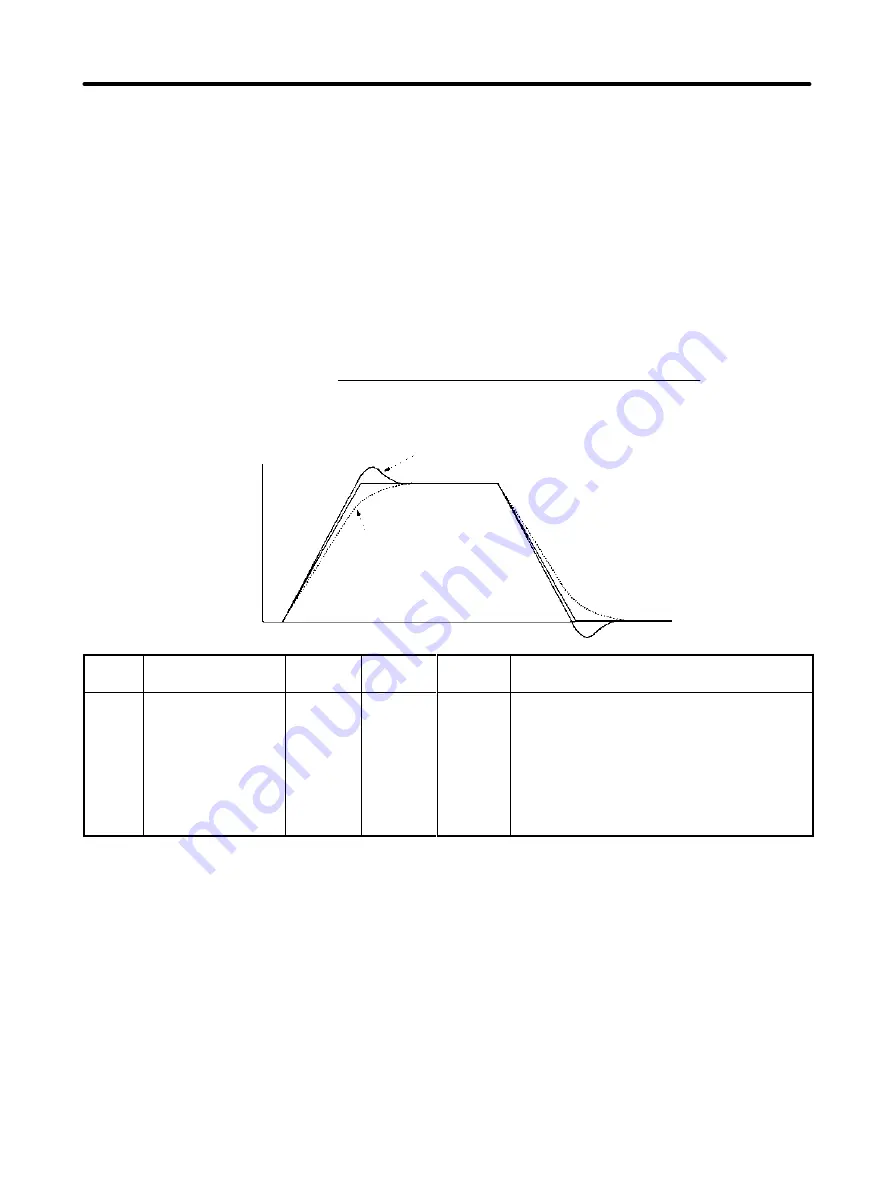
The response is as shown in the following diagram when the position loop gain is manipulated.
Motor speed
High position loop gain
Low position loop gain
Time
PRM
No.
Parameter name
Factory
setting
Unit
Setting
range
Explanation
Cn-1b
Positioning comple-
tion range
3
Com-
mand
units
0 to 250
Sets the range for the positioning comple-
tion signal output. (Generally set according
to the precision required by the system.)
Increasing the positioning completion range
too much can cause the positioning
completion output to turn ON during low-
speed operation or other times when there
are few residual pulses.
j
Feed-forward Amount
The feed-forward amount is effective when the position loop gain is set to less than 25 l/s. It will not be
very effective when the position loop gain is higher than 25 l/s.
Increasing the feed-forward amount to much will cause excessive overshooting.
The feed-forward amount is not sent through the deviation counter, but is applied directly to the speed
loop. The differential of the deviation counter is thus not applied, causing a faster response when the
load response is delayed from the commands.
Be sure that the position loop is completely adjusted and that the speed loop is operating safely before
adjusting the feed-forward amount.
Increasing the feed-forward amount too much will cause the speed command to oscillate, resulting in
abnormal noise from the motor. Increase the feed-forward amount slowly from 0%, adjusting it so that
Operation
Chapter 3
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com
















































