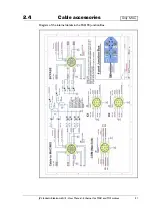
38
JVL Industri Elektronik A/S - User Manual - Ethernet for MAC and MIS motors
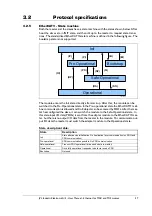
3.2.6
CANopen over EtherCAT®
The application layer communication protocol in EtherCAT® is based on the CANopen
DS 301 communication profile and is called CANopen over EtherCAT® (CoE). The pro-
tocol specifies the Object Dictionary in the adapter module, in addition to communica-
tion objects for exchanging cyclic process data and acyclic messages. In addition to DS301
and the default JVL profile, the MAC00-ECx also supports the DSP402 drive profile
DSP-402 drive profile, page 53
The EtherCAT® module uses the following message types:
• Process Data Object (PDO). The PDO is used for cyclic I/O communication,
in other words, process data.
• Service Data Object (SDO). The SDO is used for much slower acyclic
data transmission.
• Emergency Object (EMCY). The EMCY is used for error reporting when a fault has
occurred in the module or in the drive.
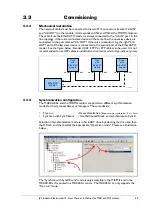
3.2.7
Drive synchronization
(only applicable to & MIS/MILxxx)
Distributed clocks
The distributed clock is the primary mechanism built into the EtherCAT network proto-
col to allow synchronization between the master and slaves in the network. Not every
EtherCAT device supports the distributed clock protocol, but those that do can use this
mechanism to share a common clock domain across the network. MAC00-ECx supports
this when mounted in a , and the MIS/MIL also supports this feature.
When the MAC00-ECx is mounted in a
MAC050 - MAC141
DC is
NOT
supported.
When the distributed clock protocol is being used, one clock on the network is selected
as the master clock, and all other devices are synchronized to it. The master controller
of the network determines which clock will be used as the master clock. The master
clock can either reside in the master controller itself, or in one of the slave devices on
the network. In many systems the slave devices are able to capture time stamps more
accurately than the master controller, so usually the first DC capable slave device in the
network is selected as the clock source.
Every EtherCAT slave device which supports the DC feature includes hardware which
allows a very accurate local time stamp to be captured when certain registers are written
over the network. These time stamps can then be used by the slave device to adjust its
local clock to remove the drift between it and the master clock on the network.
The EtherCAT master uses these time stamps to calculate the network delay between
devices on the network and to find an offset between each slave's local time and the sys-
tem time.
Once this offset has been found for each slave, the master writes the offset to a register
on the slave's EtherCAT interface hardware. The result is a shared time base for every
device on the network which supports the distributed clock protocol.
Summary of Contents for MAC00-EC4
Page 2: ......
Page 14: ...14 JVL Industri Elektronik A S User Manual Ethernet expansion modules for MAC motors ...
Page 32: ...32 JVL Industri Elektronik A S User Manual Ethernet for MAC and MIS motors ...
Page 78: ...78 JVL Industri Elektronik A S User Manual Ethernet for MAC and MIS motors ...
Page 136: ...136 JVL Industri Elektronik A S User Manual Ethernet for MAC and MIS motors ...
Page 176: ...176 JVL Industri Elektronik A S User Manual Ethernet for MAC and MIS motors ...
Page 177: ...JVL Industri Elektronik A S User Manual Ethernet for MAC and MIS motors 177 8 Sercos ...
Page 224: ...224 JVL Industri Elektronik A S User Manual Ethernet for MAC and MIS motors ...
Page 241: ...JVL Industri Elektronik A S User Manual Ethernet for MAC and MIS motors 241 ...
Page 252: ...252 JVL Industri Elektronik A S User Manual Ethernet for MAC and MIS motors ...
Page 256: ...256 JVL Industri Elektronik A S User Manual Ethernet for MAC and MIS motors ...
Page 257: ...JVL Industri Elektronik A S User Manual Ethernet for MAC and MIS motors 257 12 Appendix ...