ifm
System Manual
ecomat
mobile
SmartController (CR2500) V05
PWM in the ecomatmobile controller
PWM signal processing
161
9.1
PWM signal processing
The abbreviation PWM stands for
p
ulse
w
idth
m
odulation. It is mainly used to trigger proportional
valves (PWM valves) for mobile and robust controller applications. Also, with an additional component
(accessory) for a PWM output the pulse-width modulated output signal can be converted into an
analogue output voltage.
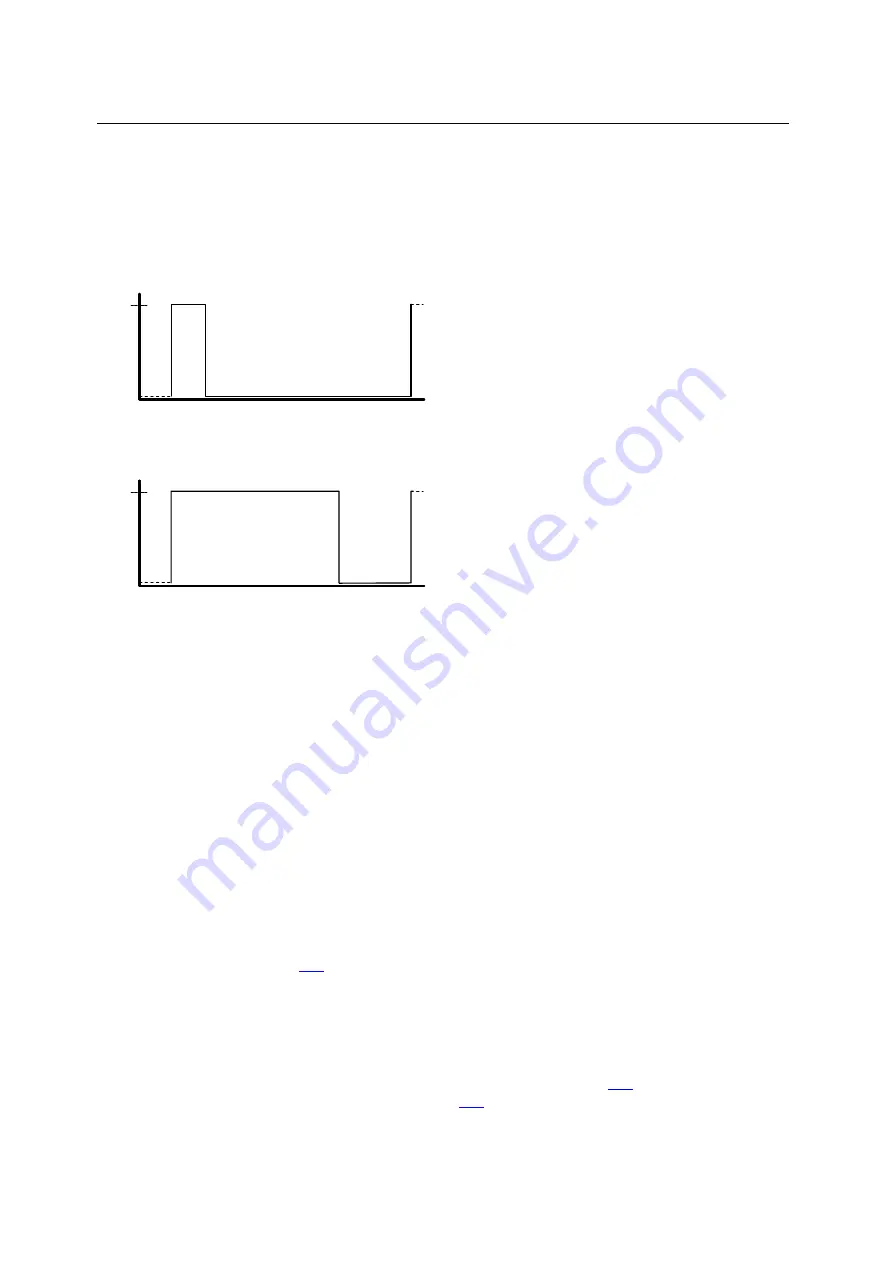
U
B
15% Ein
ON
85% Aus
OFF
U
B
70% Ein
ON
30% Aus
OFF
Figure: PWM principle
The PWM output signal is a pulsed signal between GND and supply voltage. Within a defined period
(PWM frequency) the mark-to-space ratio is then varied. Depending on the mark-to-space ratio, the
connected load determines the corresponding RMS current.
The PWM function of the
ecomat
mobile
controller is a hardware function provided by the processor.
To use the integrated PWM outputs of the controller, they must be initialised in the application program
and parameterised corresponding to the requested output signal.
9.1.1
PWM functions and their parameters (general)
PWM / PWM1000
Depending on the application and the requested resolution, the function PWM or PWM1000 can be
selected for the application programming. High accuracy and thus resolution is required when using
the control functions. This is why the more technical PWM function is used in this case.
If the implementation is to be kept simple and if there are no high requirements on the accuracy, the
function PWM1000 (
→
page
) can be used. For this function the PWM frequency can be directly
entered in [Hz] and the mark-to-space ratio in steps of 1 ‰.
PWM frequency
Depending on the valve type, a corresponding PWM frequency is required. For the PWM function the
PWM frequency is transmitted via the reload value (function PWM,
→
) or directly as a
numerical value in [Hz] (function PWM1000,
→
page
). Depending on the controller, the PWM
outputs differ in their operating principle but the effect is the same.















































