12: M
ODBUS
ASCII/RTU C
OMMUNICATION
FC5A M
ICRO
S
MART
U
SER
’
S
M
ANUAL
FC9Y-B1268
12-7
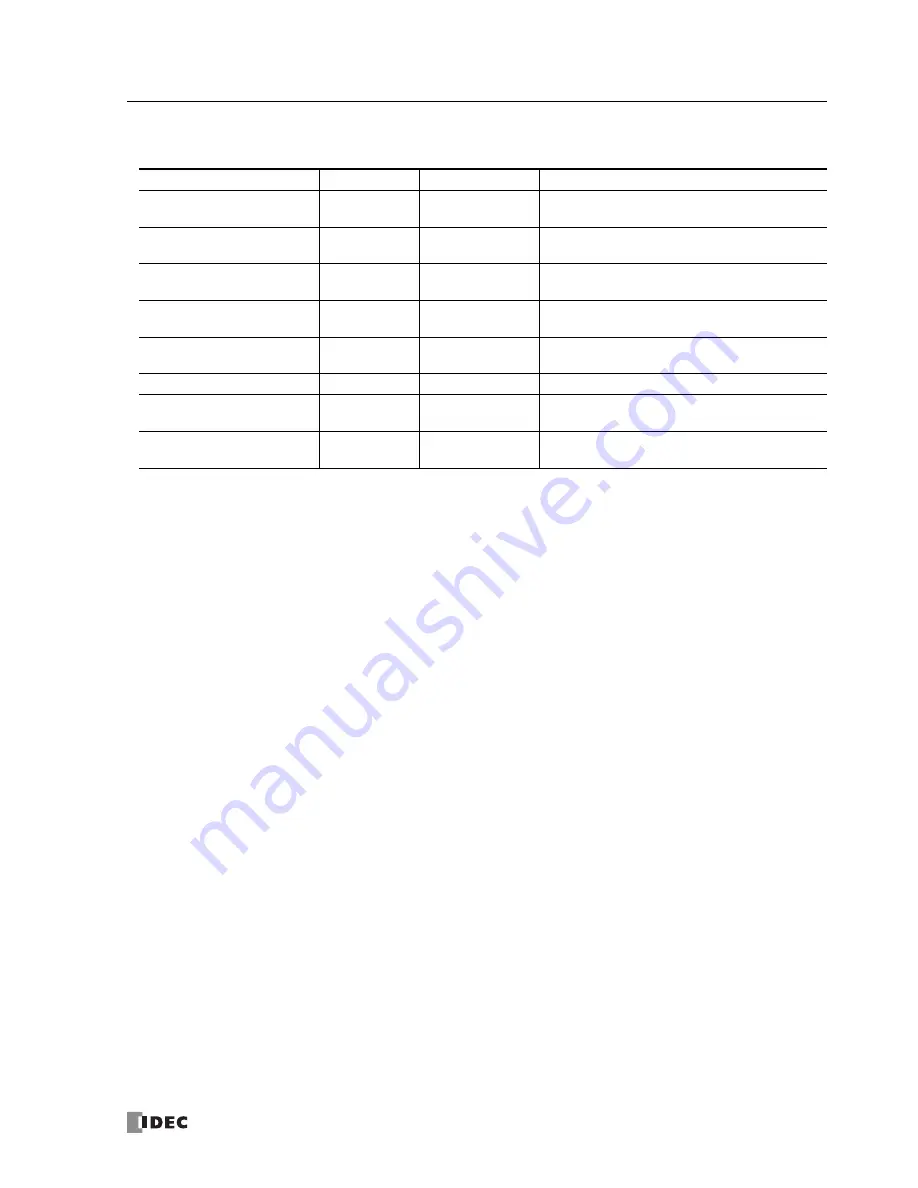
Function Code
The MicroSmart accepts eight function codes as listed in the table below:
Function Code
Data Size
Slave Address
MicroSmart as Modbus Slave
01 Read Coil Status
1 to 128 bits
000001 - 065535
Reads bit device statuses of Q (output), R (shift regis-
ter), or M (internal relay).
02 Read Input Status
1 to 128 bits
100001 - 165535
Reads bit device statuses of I (input), T (timer con-
tact), or C (counter contact).
03 Read Holding Registers
1 to 64 words
400001 - 465535
Reads word device data of D (data register), T (timer
preset value), or C (counter preset value).
04 Read Input Registers
1 to 64 words
300001 - 365535
Reads word device data of T (timer current value) or
C (counter current value).
05 Force Single Coil
1 bit
000001 - 065535
Changes a bit device status of Q (output), R (shift
register), or M (internal relay).
06 Preset Single Register
1 word
400001 - 465535
Changes word device data of D (data register).
15 Force Multiple Coils
1 to 128 bits
000001 - 065535
Changes multiple bit device statuses of Q (output), R
(shift register), or M (internal relay).
16 Preset Multiple Registers
1 to 64 words
400001 - 465535
Changes multiple word device data of D (data regis-
ter).
Master Device Address
When function code 01, 02, 03, or 04 is selected to read data from Modbus slaves, designate the first data register or
internal relay number to store the data received from the Modbus slave. When function code 05, 06, 15, or 16 is selected
to write data to Modbus slaves, designate the first data register or internal relay number to store the data to write to the
Modbus slave. Data registers and internal relays can be designated as the master device address.
Data Size and Word/Bit
Designate the quantity of data to read or write. The valid data size depends on the function code. When function code
01, 02, 05, or 15 is selected, designate the data size in bits. When function code 03, 04, 06, or 16 is selected, designate
the data size in words. For valid data sizes, see the table above.
Slave No.
Designate slave numbers 0 through 247. The same slave number can be designated repeatedly for different request num-
bers which can be 1 through 255 (or 2040 on CPU modules with system program version 110 or higher). In the Modbus
communication, slave number 0 is used for a broadcast slave number.
Slave Address
Designate data memory addresses of Modbus slaves. The valid slave address range depends on the function code. For
valid slave addresses, see the table above.
Request Execution Device
To use request execution devices, click the radio button for “Use” and designate the first internal relay number in the
Modbus ASCII or RTU Master Request Table. Devices used for executing requests are automatically listed in the table. To
execute a request, turn on the corresponding request execution device.
Slim type CPU modules with system program version 110 or higher can also designate data registers the Request Execu-
tion Device. When the first data register number is designated as the Request Execution Device, data register bits as
many as the number of requests are allocated from the least significant bit of the first data register. Data register bits
assigned as the execution relays are automatically listed in the Request Table.
When request execution devices are not designated, all requests programmed in the Request Table are executed continu-
ously.
Error Status Data Register
To use error status data registers, click the radio button for “Use” and designate the first data register number in the
Modbus ASCII or RTU Master Request Table. Data registers used for storing error statuses are automatically listed in the
table. When Use a single DR for all communication requests is selected, the first data register is shared by all requests.
Phone: 800.894.0412 - Fax: 888.723.4773 - Web: www.clrwtr.com - Email: [email protected]
















































