Rev. 1.10
136
October 23, 2020
Rev. 1.10
137
October 23, 2020
BC66F5652
2.4GHz RF Transceiver A/D Flash MCU
BC66F5652
2.4GHz RF Transceiver A/D Flash MCU
A/D Converter Input Signals
All of the external A/D analog input pins are pin-shared with the I/O pins as well as other functions.
The corresponding pin-shared function selection bits in the PxS1 and PxS0 registers, determine
whether the external input pins are set as A/D converter analog channel inputs or whether they have
other functions. If the corresponding pin is setup to be an A/D converter analog channel input, the
original pin functions will be disabled. In this way, pins can be changed under program control to
change their function between A/D inputs and other functions. All pull-high resistors, which are
setup through register programming, will be automatically disconnected if the pins are setup as A/
D
converter inputs. Note that it is not necessary to first setup the A/D pin as an input in the port
control register to enable the A/D converter input as when the relevant A/D converter input function
selection bits enable an A/D converter input, the status of the port control register will be overridden.
As the device contains only one actual analog to digital converter hardware circuit, each of the
external and internal analog signals must be routed to the converter. The SAINS3~SAINS0 bits in
the SADC1 register are used to determine that the analog signal to be converted comes from the
external channel input or internal analog signal. The SACS3~SACS0 bits in the SADC0 register are
used to determine which external channel input is selected to be converted. If the SAINS3~SAINS0
bits are set to “0000”, the external channel input will be selected to be converted and the
SACS3~SACS0 bits can determine which external channel is selected.
When the SAINS field is set to the value of “0x01”, “0x10” or “0x11”, the internal analog signal will
be selected. If the internal analog signal is selected to be converted, the external channel signal input
will automatically be switched off regardless of the SACS field value. It will prevent the external
channel input from being connected together with the internal analog signal.
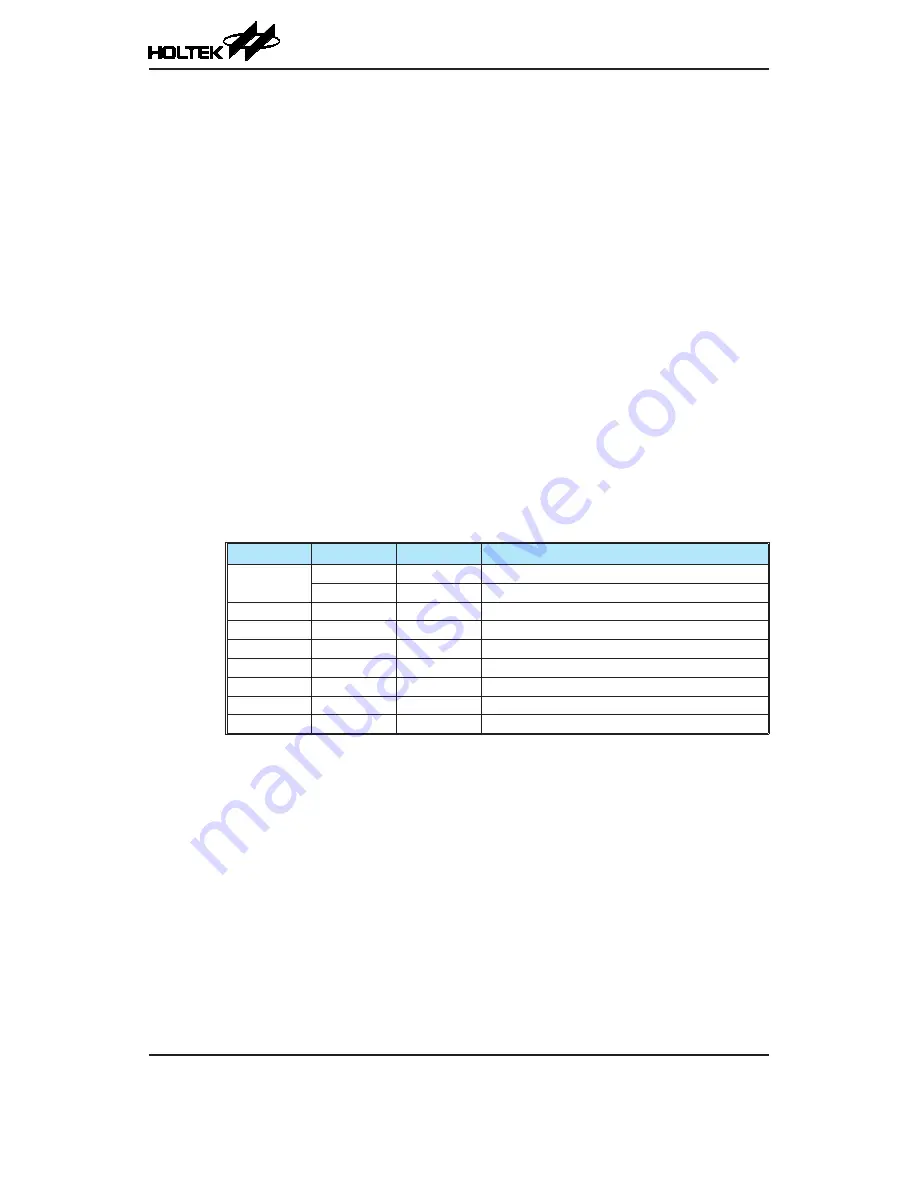
SAINS[3:0]
SACS[3:0]
Input Signals
Description
0000, 0100,
11xx
0000~1011
AN0~AN11 External channel analog input ANn
1100~1111
—
Floating, no external channel is selected
0001
xxxx
AV
DD
Internal A/D converter power supply voltage AV
DD
0010
xxxx
AV
DD
/2
Internal A/D converter power supply voltage AV
DD
/2
0011
xxxx
AV
DD
/4
Internal A/D converter power supply voltage AV
DD
/4
0101
xxxx
V
R
Internal A/D converter PGA output V
R
0110
xxxx
V
R
/2
Internal A/D converter PGA output V
R
/2
0111
xxxx
V
R
/4
Internal A/D converter PGA output V
R
/4
10xx
xxxx
GND
Connected to the ground
A/D Converter Input Signal Selection
A/D Converter Operation
The START bit in the SADC0 register is used to start the A/D conversion. When the microcontroller
sets this bit from low to high and then low again, an analog to digital conversion cycle will be initiated.
The ADBZ bit in the SADC0 register is used to indicate whether the analog to digital conversion
process is in process or not. This bit will be automatically set to “1” by the microcontroller after an
A/D conversion is successfully initiated. When the A/D conversion is complete, the ADBZ will be
cleared to “0”. In addition, the corresponding A/D
converter interrupt request flag will be set in the
interrupt control register, and if the interrupts are enabled, an appropriate internal interrupt signal
will be generated. This A/D converter
internal interrupt signal will direct the program flow to the
associated A/D converter internal interrupt address for processing. If the A/D converter internal
interrupt is disabled, the microcontroller can be used to poll the ADBZ bit in the SADC0 register to
check whether it has been cleared as an alternative method of detecting the end of an A/D conversion
cycle.
















































