A
29
App
e
ndix
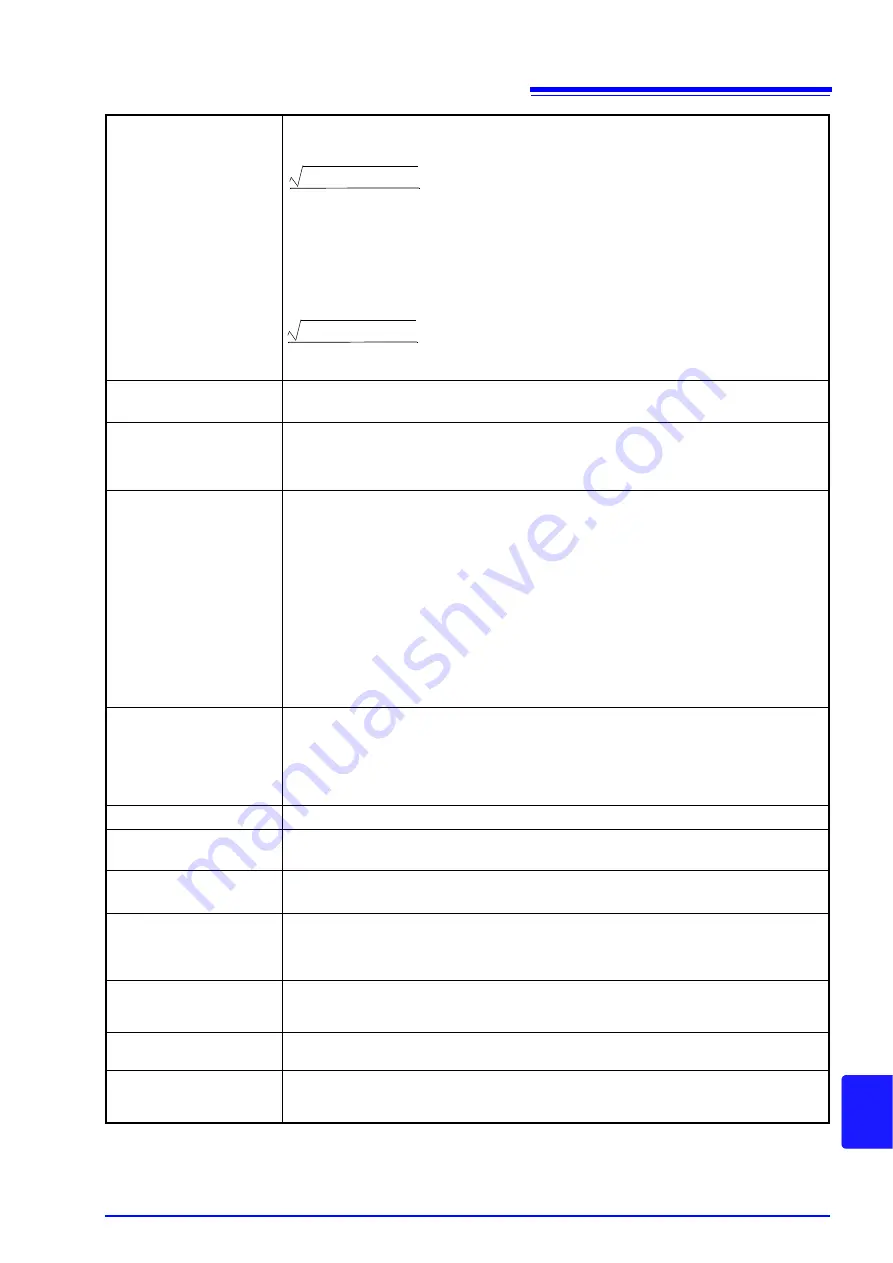
Total harmonic
distortion factor
THD-F:
The ratio of the size of the total harmonic component to the size of the fundamental wave,
expressed as a percentage using the following equation:
(for the PQ3198, calculated to the 50th order)
This value can be monitored to assess waveform distortion for each item, providing a yard-
stick that indicates the extent to which the total harmonic component is distorting the fun-
damental waveform. As a general rule, the total distortion factor for a high-voltage system
should be 5% or less; it may be higher at the terminal point of the system.
THD-R:
The ratio of the size of the total harmonic component to the size of RMS values, expressed
as a percentage using the following equation:
(for the PQ3198, calculated to the 50th order)
THD-F is typically used.
Measurement
frequency (fnom)
The nominal frequency of the system being measured. Select from 50 Hz/60 Hz/400 Hz.
(The measurement frequency is automatically set during the quick setup process.)
Timer event function
Functionality for generating events at a set time interval and recording the measured value
and event waveform at that time. This function allows you to capture instantaneous wave-
forms and other data regularly, even if no abnormalities have occurred. Use this functional-
ity when you wish to record a waveform at a fixed time interval.
Multiple-phase system
treatment
Method for defining the start and end of events such as dips, swells, and interruptions in
multiple-phase systems, for example systems with 3 phases
Dip:
A dip begins when the voltage of at least one channel is less than or equal to the threshold
and ends when voltage readings for all measurement channels exceed (thr hyster-
esis voltage).
Swell:
A swell begins when the voltage of at least one channel exceeds the threshold and ends
when voltage readings for all measurement channels are less than or equal to (thr
hysteresis voltage).
Interruption:
An interruption begins when voltage readings for all channels are less than or equal to the
threshold and ends when the voltage of a user-specified channel is greater than or equal to
(thr hysteresis).
Dip
A short-lived voltage drop caused by the occurrence of a inrush current with a large load,
such as when a motor starts. When recording voltage and current trends at the power ser-
vice inlet, you can determine whether you should look for the cause of the dip inside or out-
side the building. If the voltage drops while the building's current consumption rises, the
cause likely lies inside the building. If the voltage and current are both low, the cause is
likely to lie outside the building.
Text data
A file containing only data expressed using characters and character codes.
RMS voltage refreshed
each half-cycle
The RMS value of one voltage waveform overlapped every half-cycle.
RMS current refreshed
each half-cycle
The RMS value of the current waveform every half-cycle.
Inrush current
A large current that flows temporarily, for example when an electric device is turned on. A
inrush current can be equal to or greater than 10 times the current that flows when the
device is in the normal operating state. Inrush current measurement can be a useful diag-
nostic when setting circuit breaker capacity.
Transient overvoltage
An event caused by lightning strikes, circuit-breaker and relay contact obstructions and
tripping, and other phenomena. Transient overvoltages are often characterized by precipi-
tous voltage variations and a high peak voltage.
Binary data
All data other than text (character) data. Used when analyzing data with the included PQ
ONE application.
Apparent power
The (vector) power obtained by combining active power and reactive power. As its name
suggests, apparent power expresses the “visible" power and comprises the product of the
voltage and current RMS values.
Σ
(from 2nd order)
2
fundamental wave
×
100 [%]
Σ
(from 2nd order)
2
RMS value
×
100 [%]
HIOKI PQ3198A961-03
Summary of Contents for PQ3198
Page 2: ...HIOKI PQ3198A961 03...
Page 6: ...Contents iv HIOKI PQ3198A961 03...
Page 20: ...Usage Notes 14 HIOKI PQ3198A961 03...
Page 44: ...2 3 Display Items and Screen Types 38 HIOKI PQ3198A961 03...
Page 58: ...3 8 Turning the Power On and Off Setting the Default Language 52 HIOKI PQ3198A961 03...
Page 102: ...5 8 Factory Settings 96 HIOKI PQ3198A961 03...
Page 198: ...12 4 Downloading Recorded Data to Computer 192 HIOKI PQ3198A961 03...
Page 264: ...14 4 Disposing of the Instrument 258 HIOKI PQ3198A961 03...
Page 296: ...A32 HIOKI PQ3198A961 03...
Page 299: ...Index Index 3 Index Wiring 73 Z Zero adjustment 53 Zero phase A28 HIOKI PQ3198A961 03...
Page 300: ...Index Index 4 HIOKI PQ3198A961 03...
Page 301: ...HIOKI PQ3198A961 03...
Page 302: ...HIOKI PQ3198A961 03...
Page 303: ...HIOKI PQ3198A961 03...
Page 304: ...www hioki com HIOKI PQ3198A961 03...












































