Documentation HG G-73650ZD | English, Revision 05 | Date: 09.03.2017 | www.goetting-agv.com
60
Chapter 4: Software
4.3.3.1 What type of vehicle is involved?
–
If the vehicle has an axle that cannot be steered independently, it is
not an omnidirec-
tional vehicle
.
–
Vehicles with two axles that can only be steered symmetrically are
not omnidirec-
tional vehicles,
as there is a point between the two axles at which a rigid axle could
be deployed.
–
If the vehicle has axles that can only be steered independently, it is
an omnidirec-
tional vehicle
.
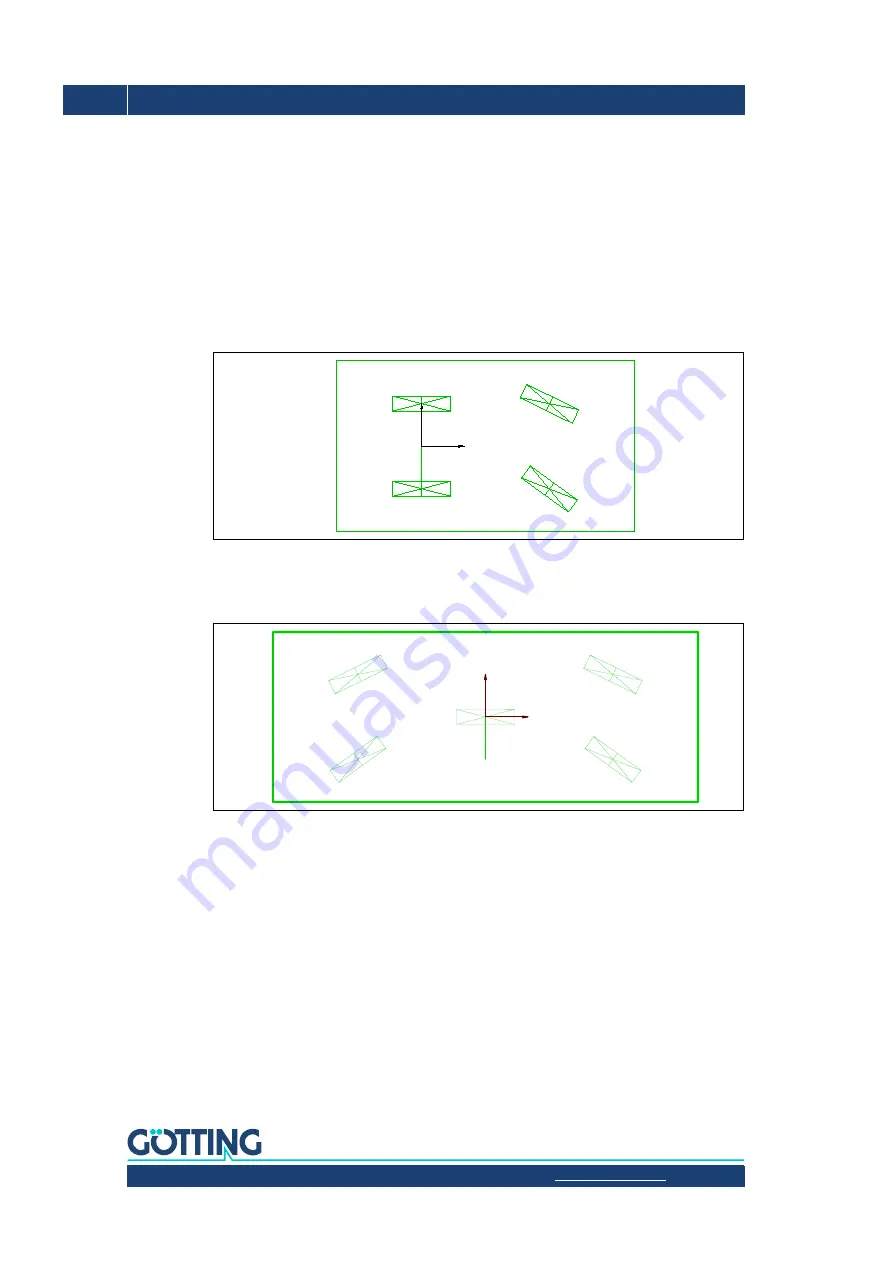
4.3.3.2 The non-omnidirectional vehicle
Figure 50
Example: Non-omnidirectional vehicle
In the case of these vehicles,
the vehicle zero point must be on the axle that cannot
be steered
. The wheels that cannot be steered must be of the type
Fix. Angle.
Figure 51
Example: Symmetrically steerable axles (non-omnidirectional vehicle)
This vehicle is not omnidirectional either, as a rigid axle could be drawn in the middle. On
these vehicle, instead of the rear wheels, the middle wheel, which in reality is not present,
must be set in the parameters (wheel of the type
Fix. Angle
so that the navigation controller
applies the corresponding controller).
The vehicle zero point must be located on the
virtual rigid axle.
Vehicle X
Vehicle Y
Front
Example:
Vehicle X
Vehicle Y
Front
Example:
















































