2 - 26
Description varix 200/varix 14 (DECT)
2 Planning a cordless communications network
2.9.2
Multiple-path signal propagation and associated bit interference
(ISI – inter-symbol interference)
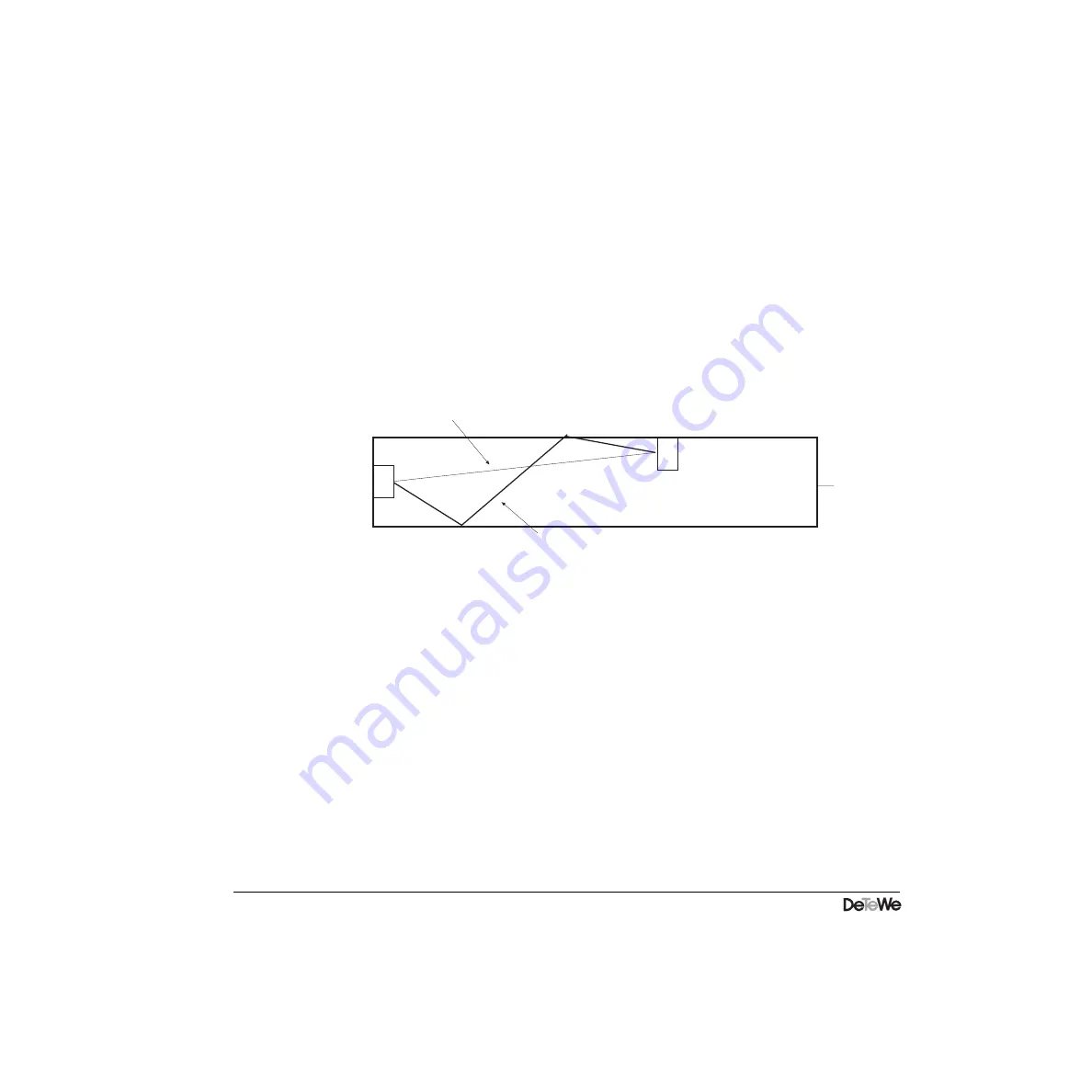
The general environment and buildings in the vicinity of the base stations (FPs) and the PPs
lead to signal deflections, scatter and reflections which cause the signal to reach the receiver
by a multitude of paths. This multiple-path propagation means that the signal reaches the
receiver with different propagation time delays and attenuation. The following diagram (fig.
2.16) shows the principle based on the plan view of an office floor.
The overall signal received is the sum of the direct signal and all the different delayed and
correspondingly attenuated echoes of the signal received due to the multiple propagation
paths. The superimposition of these signal echoes leads to ”inter-symbol interference” (ISI) or
bit interference. This means that the signal which reaches the receiver after undergoing multi-
ple reflections arrives at a time at which a new ”symbol” (e.g. bit or sequence of bits) has
already reached the same receiver by the direct path, which means that the reflected signal
will interfere with the direct signal.
FP
outer wall
of building
PP
signal path via multiple reflections
direct signal path
Fig. 2.16
















































