M-4272 Instruction Book
1–8
Hot Parallel, Fast, In-Phase, Residual and
Fixed Time Transfer Methods
MBTs can be categorized as closed or open transition
[2]. The closed transition involves brief paralleling
of the sources. The closed transition transfer is
commonly referred to as a hot parallel transfer.
Open transition transfers do not parallel the sources,
and include fast, in-phase, residual and fixed time.
The fast transfer can be subcategorized as
simultaneous or sequential. All other transfers are
sequential.
Hot Parallel Transfer
In a hot parallel transfer, the new source is
connected to the motor bus before the old source is
tripped. The intent is to transfer sources without
interruption. The phase angle, delta voltage and
delta frequency from the motor bus and the new
source are evaluated prior to the transfer to assure
that the motor bus and the new source are in
synchronism. This method has gained wide
acceptance for routine source transfers because
transients on the motor bus are eliminated.
There may be instances where the two sources
may not be derived from the same primary source
and a large standing phase angle may be present
between them, precluding a hot parallel transfer.
Assuming the two sources’ phase angle relationship
is acceptable, with the two sources paralleled,
currents flowing into and through the bus may violate
the interrupt rating for the circuit breakers and the
short term withstand ratings of the source
transformers. A fault occurring either on the bus or
on one of the sources during the time the sources
are paralleled can overstress the components of
the bus system. The probability of this happening
may be viewed as small; however, the consequences
of such a fault occurring during the source paralleled
operating interval should be thoroughly understood
before the hot parallel transfer system is used.
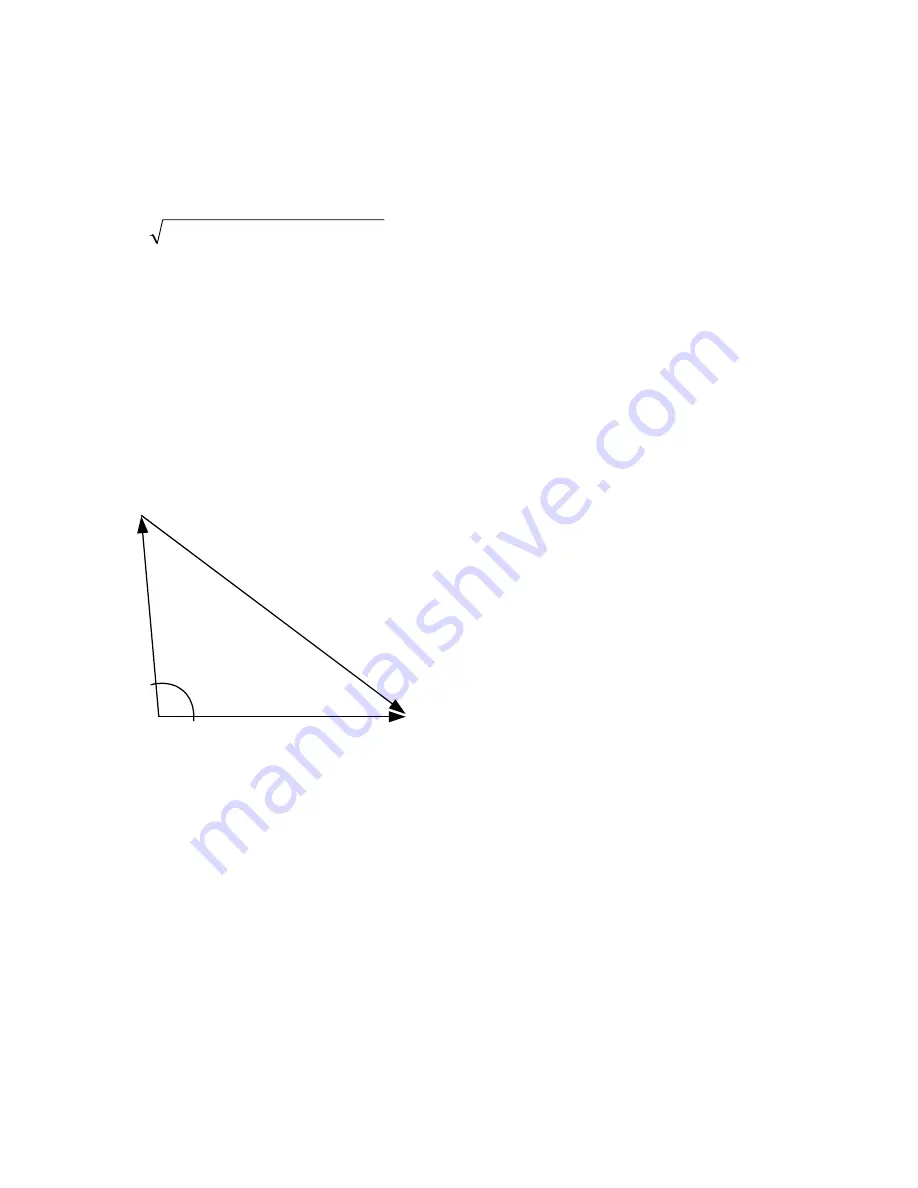
The resultant V/Hz issue is exacerbated when the
phase angle difference increases and the voltage
difference increases as shown in Figure 1-8. The
following relationship in equation 1 defines this
condition:
θ
cos
2
2
2
M
S
M
S
R
E
E
E
E
E
−
+
=
[1]
where
E
S
System equivalent V/Hz
E
M
Motor residual V/Hz (on system base)
E
R
Resultant vectorial V/Hz
q Phase angle between the motor bus and
new source at the instant prior to
connection
E
S
= 1 pu @ 0 degrees
E
R
= 1
.33
pu
E
M
=
0
.8
1
p
u
@
-9
5 d
eg
re
es
Figure 1-8 V/Hz Resultant Between E
S
and E
M
Summary of Contents for M-4272
Page 1: ...Instruction Book Book 1 of 2 M 4272 Motor Bus Transfer System ...
Page 45: ...xviii M 4272 Instruction Book This Page Left Intentionally Blank ...
Page 200: ...System Setup and Setpoints 4 4 89 Figure 4 93 ISSLogic Function Dialog Screen ...
Page 207: ...M 4272 Instruction Book 4 96 This Page Left Intentionally Blank ...
Page 214: ...Declaration of Conformity Appendix I I 1 IAppendix I Declaration of Conformity ...
Page 215: ...M 4272 Instruction Book I 2 This Page Left Intentionally Blank ...
















































