Zynq-7000 AP SoC and 7 Series FPGAs MIS v4.1
439
UG586 November 30, 2016
Chapter 3:
RLDRAM II and RLDRAM 3 Memory Interface Solutions
The
wr_en
signals are required to be asserted an extra clock cycle before the first
wr_en
signal is asserted, and held for an extra clock cycle after deassertion. This ensures that the
shared bus has time to change from read to write and from write to read. The physical layer
has a requirement of two clock cycles of no operation (NOP) when transitioning from a write
to a read, and from a read to a write. This two clock cycle requirement depends on the PCB
and might need to be increased for different board layouts.
Memory Controller
The Memory Controller enforces the RLDRAM II/RLDRAM 3 access requirements and
interfaces with the PHY. The controller processes commands in order, so the rank of
commands presented to the controller is the order in which they are presented to the
memory device.
The Memory Controller first receives commands from the user interface and determines if
the command can be processed immediately or needs to wait. When all requirements are
met, the command is placed on the PHY interface. For a write command, the controller
generates a signal for the user interface to provide the write data to the PHY. This signal is
generated based on the memory configuration to ensure the proper command-to-data
relationship. Auto-refresh commands are inserted into the command flow by the controller
to meet the memory device refresh requirements.
For CIO devices, the data bus is shared for read and write data. Switching from read
commands to write commands and vice versa introduces gaps in the command stream due
to switching the bus. For better throughput, changes in the command bus should be
minimized when possible.
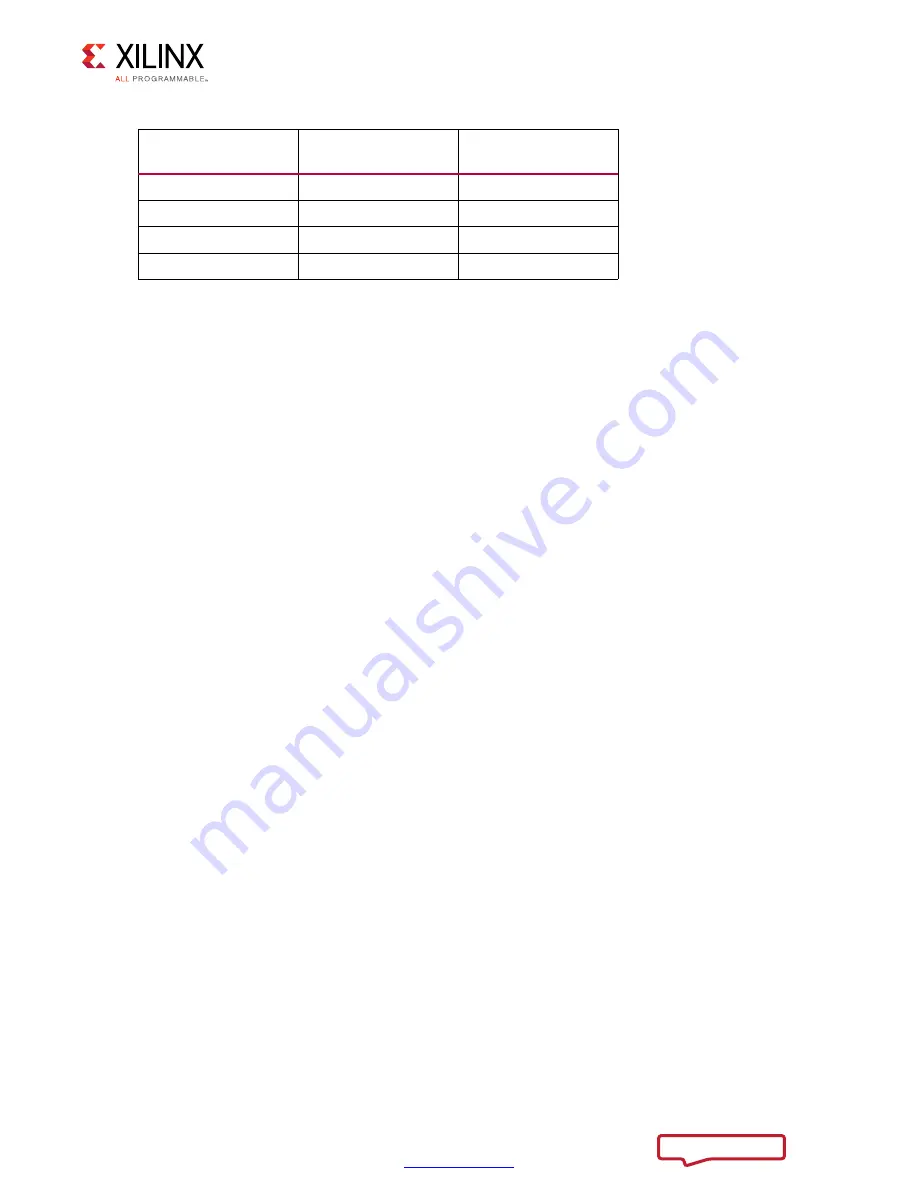
3
5
OFF
1
2
2
3
3
4
Notes:
1. Shown in
.
Table 3-13:
RLDRAM II Command to Write Enable Timing
(Cont’d)
Address Multiplexing
Configuration
Command to Write
Enable (Clock Cycles)
















































