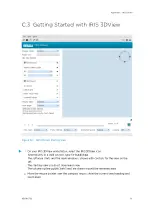
3. Use your mouse to control the 3D view:
• Hold the left mouse button and drag the mouse to move the camera position about
the center of the picture.
The camera remains aiming at the center, so this effectively rotates the data.
Drag the mouse horizontally to rotate the camera about the center.
Drag the mouse vertically to move the camera vertically about the center.
• Hold the right mouse button and drag the mouse to move the camera location.
The camera pointing angle remains the same so this pans the data. Holding the left
button and shift key does the same.
• Hold the middle mouse button and drag the mouse (or rotate the mouse wheel) to
move the camera closer or farther from the center. This effectively zooms the data.
4. To save your own view angle presets, use the view angle preset manager.
See
Managing the IRIS 3D Display (page 323)
.
5. To return to the starting view at any time, select the default angle preset.
C.4 Opening Data Files in IRIS 3DView
1. Make sure the data file locations are configured in IRIS 3D
Settings
.
See
Managing IRIS 3DView Settings (page 332)
2. To open a data file, select
File > Open 3D data
.
This opens the 3D data selector where you can select the data file.
3. To open the file in
Live
mode, select
Display mode > Live
.
In
Live
mode, IRIS 3DView opens the latest data file from the radar site selected in the
Radar site
drop-down list.
See
Managing the IRIS 3D Display (page 323)
.
C.5 Rendering Modes
Rendering mode determines the visualization approach that IRIS 3DView takes when
creating the 3D model of the radar data.
You choose the rendering mode and the mode-specific options in the
Settings
window. For
rendering, you can choose from surface rendering and volume rendering.
IRIS 3DView uses a full spectrum color scale when rendering the radar data. Blues represent
the weakest echoes, building up to greens, yellows, oranges, and finally reds. The color scale
is NOT absolute, it is relative. The reflectivity legend on the product information tool window
shows the current relationship of colors and reflectivity in decibels (dBZ).
C.5.1 Surface Rendering
Surface rendering mode uses what in 3D terminology are called iso-surfaces. In other words,
for example, if the threshold of the first iso-surface is set at 30 dBZ, all of the echo that is
less than 30 dBZ is removed from the picture and what you see is a shape that represents
the outer boundary of the 30 dBZ echo.
IRIS Product and Display User Guide
M211319EN-H
320
RESTRICTED
Содержание IRIS
Страница 1: ...M211319EN H RESTRICTED User Guide IRIS Radar IRIS Product and Display...
Страница 12: ...IRIS Product and Display User Guide M211319EN H 10 RESTRICTED...
Страница 71: ...Chapter 3 Configuring IRIS Products RESTRICTED 69...
Страница 294: ...To add icons you must include a text next to the icon IRIS Product and Display User Guide M211319EN H 292 RESTRICTED...
Страница 303: ...Figure 103 Typical Spectrum Plot Appendix A Basic Radar Meteorology RESTRICTED 301...
Страница 324: ...Figure 109 Example of Volume Rendering IRIS Product and Display User Guide M211319EN H 322 RESTRICTED...
Страница 329: ...C 8 Using the Product Information Tool Figure 113 Product Information Tool Appendix C IRIS 3DView RESTRICTED 327...
Страница 386: ......
Страница 392: ......
Страница 393: ......
Страница 394: ...www vaisala com...