Copyright © Siemens AG 2010. All rights reserved.
Page
46
ERTEC 400 Manual
Technical data subject to change
Version 1.2.2
4.6 UART1/ UART2
Two UARTs are implemented in the ERTEC 400. The inputs and outputs of the UARTs are available as an
alternative function at GPIO port [13:9] (UART1) and GPIO port [18:14] (UART2). For this purpose, the I/O must
be assigned to the relevant inputs and outputs and the alternative function must be assigned (see GPIO register
description). If the UARTs are used, the pins are no longer available as standard I/O. The baud rate generation is
derived from the internal 50 MHz APB clock. The data bit width for read/write access on the APB bus is 8 bits.
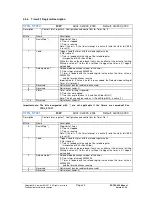
The following signal pins are available for UART 1 and UART 2 on the ERTEC 400.
•
Transmit cable
1 per UART
TXD1/TXD2
•
Receive cable
1 per UART
RXD1/ RXD2
•
Handshake
3 per UART
DCD1_N/DCD2_N
CTS1_N/CTS2_N
DSR1_N/DSR2_N
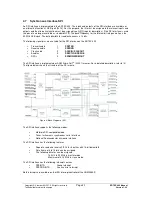
Both UARTs are implemented as ARM Prime Cell
TM
(PL010) macros. These are similar to standard UART
16C550. For a detailed description, refer to /5/.
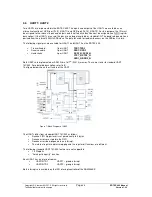
The figure below shows the structure of the UART.
Figure 7: Block Diagram of UART
The UARTs differ from standard UART 16C550 as follows:
•
Receive FIFO trigger level is set permanently to 8 bytes.
•
Receive errors are stored in the FIFO.
•
Receive errors do
not
generate an interrupt.
•
The internal register address mapping and the register bit functions are different.
The following standard UART 16C550 features are not supported:
•
1.5 Stop bits
•
“Forcing stick parity” function
Each UART has an interrupt source:
•
UARTINTR 1
UART1 – group interrupt
•
UARTINTR 2
UART2 – group interrupt
Both interrupts are available on the IRQ interrupt controller of the ARM946E-S.