Tel: 886.2.2175 2930 Email: [email protected]
www.salukitec.com
171
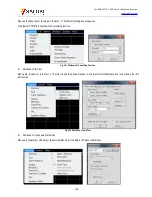
The more times averaging is done, the more noise will be reduced, and the larger the dynamic range will be. As shown in Fig. 6.5,
sweep averaging has influence on measurement results.
Fig. 6.5 Influence of Scanning Averaging on Measurement Results
Reduction of random noise
The average value of measurement can be independently set for each channel.
The total measurement time increases along with the increase of averaging times.
General noise can be minimized by setting the average value and IF bandwidth.
In order to minimize the low-frequency noise, measurement averaging is more effective than reduction of the system bandwidth.
b) Setting of sweep average value
Menu path: [Response] > [Average]. Set the average value by the [Average] key in the auxiliary menu bar or in the [Average] dialog
box. Enable or disable the averaging function by [Average on/OFF]. Directly enter the value or press the arrow button to
increase/decrease the averaging times according to the averaging factor.
Select [Restart average] to start a group of new average sweep.
6.4.
Improvement of Measurement Results of Electrical Long Device
The frequency of the signal from the tested device may be different from the frequency of the signal into the tested device at the given
time. This may result in inaccurate measurement results sometimes. The following contents can help to understand why inaccurate
measurement results are obtained and how to compensate.
Why are inaccurate results produced as a result of delay?
The source and receiver can be locked at the same time, and sweep can be done for one frequency interval with the vector
network analyzer.
The signal through the tested device (DUT) represents different colors corresponding to different frequencies.
If the stimulus frequency passes through the tested device and the analyzer is tuned to new frequency before the signal reaches
the receiver, inaccurate measurement results will be produced.
As shown in Fig. 6.6, if a long cable is measured by the analyzer, the signal frequency of the cable end will lag behind the source
frequency of the analyzer. If the frequency offset (typically dozens of kHz) is obvious relative to the IF test bandwidth of the network
analyzer, measurement results may be wrong due to the roll-down characteristics of the IF filter.