24.12
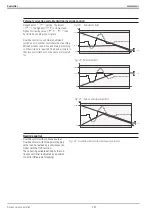
Process value calculation
Standard controller
The process variable measured via analog input
X1
is used
as process value by the controller.
Ratio controller
Process control frequently requires various components to be mixed into a product. These components must be mixed
according to a given ratio. The main component is measured and used as reference for the other components. With in-
creasing flow of the main component, the flow of the other components will increase accordingly. This means that pro-
cess value x used by the controller is determined by the ratio of two input variables
rather than
being measured as
one
process variable.
For optimum combustion, the fuel-air ratio must be controlled. With
stoichiometric combustion
, the ratio is selected so
that there are no inflammable residues in the waste gas. In this case, the relative rather than the physical ratio is dis-
played as process value and adjusted as l.
If the transmitters used by the controller are designed with a stoichiometric ratio,
λ
= 1 is met exactly with restless
combustion. With a process value display of 1,05, the instantaneous air excess is clearly 5%. The amount of air re-
quired for atomizing is taken into account by constant ‘
N0
‘. For selecting a ratio controller,
CType
=
Ratio
must
be selected. Moreover, configuration word ‘
Ratio
‘ must be taken into account.
a
With ratio controller,
note that parameters
Xn0
and
Xn100
must be set to the input range of connector X1.
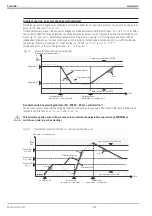
Example of standard ratio control:
Standard ratio control at the example of stoichiometric
combustion. Analog input INP1 is configured to 4...20 mA
with physical unit m
3
/h (air). Values 0 and 100 are allo-
cated to input variables 4 mA (
x0
) and 20 mA (
x100
).
Atomizing air N0 is added to this input.
E.g. INP5 is selected as second ratio input. This input is
also configured for 4...20 mA and m
3
/h (gas). x0 and x100
values 0 and 100 are allocated to the input variables.
Set-point Weff effective as relative ratio is multiplied by
stoichiometric factor
SFac
(e.g. SFac = 10), i.e. a
„stoichiometric“ flow ratio can be used for calculation of
the control deviation. The instantaneous (controlled) pro-
cess value is calculated from the physical ratio, multiplied
by 1/SFac and displayed as relative value.
9499 040 50611
Controller
197
Process value calculation
x - w
+
-
X1
weff
Содержание KS 98
Страница 8: ...Description 9499 040 50611 Construction 8...
Страница 10: ...Important technical data 9499 040 50611 Further external in and outputs 10...
Страница 12: ...Versions 9499 040 50611 I O modules for units with modular option c basic card 12...
Страница 14: ...Front view 9499 040 50611 14...
Страница 16: ...Mounting 9499 040 50611 16...
Страница 26: ...Maintenance 9499 040 50611 Further information 26...
Страница 36: ...Scaling and calculating functions 9499 040 50611 LG10 10s logarithm 36...
Страница 74: ...Signal converters 9499 040 50611 MEAN mean value formation 74...
Страница 128: ...KS98 I O extensions with CANopen 9499 040 50611 RM_DMS strain gauge module 128...
Страница 132: ...CSEND Send mod blockno s 21 23 25 27 No 57 132...
Страница 140: ...Description of KS98 CAN bus extension 9499 040 50611 140...
Страница 202: ...Controller 9499 040 50611 Process value calculation 202...