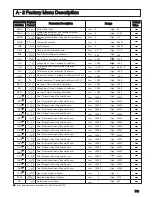
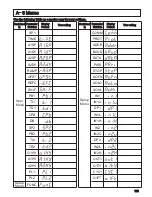
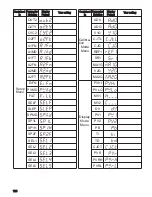
120
RFI: Radio frequency interference.
RFI: Radio frequency interference.
RS232 or RS485 output signal: A serial interface suitable
for connection between a digital control and a personal
computer, a host computer or printer.
RS232 or RS485 output signal: A serial interface suitable
for connection between a digital control and a personal
computer, a host computer or printer.
RTD: A temperature sensing probe of finely wound
platinum wire that displays a linear resistance change
for a corresponding temperature change. The resistance
increases as the temperature rises. A base resistance
of 100 ohms at 32 °F is the industry (DIN) standard.
RTD: A temperature sensing probe of finely wound
platinum wire that displays a linear resistance change
for a corresponding temperature change. The resistance
increases as the temperature rises. A base resistance
of 100 ohms at 32 °F is the industry (DIN) standard.
Saturation temperature: The boiling temperature of a
liquid at the existing pressure.
Saturation temperature: The boiling temperature of a
liquid at the existing pressure.
SCFM: Volumetric flow rate in cubic feet per minute at 60
°F (15 °C) and standard atmospheric pressure.
SCFM: Volumetric flow rate in cubic feet per minute at 60
°F (15 °C) and standard atmospheric pressure.
SCR: Silicone Controlled Rectifier
SCR: Silicone Controlled Rectifier
Secondary standard: A standard of unit measurement
derived from a primary standard.
Secondary standard: A standard of unit measurement
derived from a primary standard.
Sensitivity: The minimum change in input signal to which
an instrument can respond.
Sensitivity: The minimum change in input signal to which
an instrument can respond.
Sheath thermocouple: A thermocouple made out of
mineral-insulated thermocouple cable which has an
other metal sheath.
Sheath thermocouple: A thermocouple made out of
mineral-insulated thermocouple cable which has an
other metal sheath.
Shield: Material surrounding a conductor(s) to prevent
electrostatic or EMI from external sources.
Shield: Material surrounding a conductor(s) to prevent
electrostatic or EMI from external sources.
Slide wire feedback: A potentiometer that varies the
resistance to control a valve position.
Slide wire feedback: A potentiometer that varies the
resistance to control a valve position.
Soak: To raise the temperature of a metal object in a
heated environment to produce a metallurgical change.
Soak: To raise the temperature of a metal object in a
heated environment to produce a metallurgical change.
Soft start: Reduces voltage on initial start-up which
reduces power to the heaters. If heater has
accumulated moisture internally during a shut down,
soft start will allow heater to dry before full voltage is
applied so as to extend heater life.
Soft start: Reduces voltage on initial start-up which
reduces power to the heaters. If heater has
accumulated moisture internally during a shut down,
soft start will allow heater to dry before full voltage is
applied so as to extend heater life.
Solid State Relay (SSR): A solid state switching device
which completes or breaks a circuit electrically with no
moving parts.
Solid State Relay (SSR): A solid state switching device
which completes or breaks a circuit electrically with no
moving parts.
Span: The difference between the upper and lower limits
of a range expressed in the same units as the range.
Span: The difference between the upper and lower limits
of a range expressed in the same units as the range.
Specific gravity: The ratio of mass of any material to the
mass of the same volume of pure water at 4 °C.
Specific gravity: The ratio of mass of any material to the
mass of the same volume of pure water at 4 °C.
Set point: Control setting to achieve or maintain
temperature.
Set point: Control setting to achieve or maintain
temperature.
Specific Heat: The ratio of thermal energy required to raise
the temperature of a particle 1 degree to the thermal
energy required to raise an equal mass of water 1
degree.
Specific Heat: The ratio of thermal energy required to raise
the temperature of a particle 1 degree to the thermal
energy required to raise an equal mass of water 1
degree.
Stability: The ability of an instrument or sensor to maintain
a constant output when a constant input is applied.
Stability: The ability of an instrument or sensor to maintain
a constant output when a constant input is applied.
SSR: Solid state relay (see relay, solid state).
SSR: Solid state relay (see relay, solid state).
Tera: The prefix for one trillion (T).
Tera: The prefix for one trillion (T).
Thermal lag: The time delay in the distribution of heat
throughout a thermal system.
Thermal lag: The time delay in the distribution of heat
throughout a thermal system.
Thermistor: A temperature sensing probe made of a
mixture of metal oxides and encapsulated in epoxy or
glass. A large change in resistance is exhibited
proportional to a change in temperature. The resistance
usually decreases as temperature rises.
Thermistor: A temperature sensing probe made of a
mixture of metal oxides and encapsulated in epoxy or
glass. A large change in resistance is exhibited
proportional to a change in temperature. The resistance
usually decreases as temperature rises.
Thermocouple: A temperature sensing probe consisting
of the junction of two dissimilar metals which has a
millivolt output proportional to the difference in
temperature between the "hot" junction and the lead
wires (cold junction).
Thermocouple: A temperature sensing probe consisting
of the junction of two dissimilar metals which has a
millivolt output proportional to the difference in
temperature between the "hot" junction and the lead
wires (cold junction).
Thermal expansion: An increase in size due to an
increase in temperature expressed in units of an
increase in length or increase in size per degree, i.e.,
inches/inch/degree C.
Thermal expansion: An increase in size due to an
increase in temperature expressed in units of an
increase in length or increase in size per degree, i.e.,
inches/inch/degree C.
Thermowell: A closed-end tube designed to protect
temperature sensors from harsh environments, high
pressure, and flows. They can be installed into a system
by pipe thread or welded flange and are usually made
of corrosion-resistant metal or ceramic material
depending upon the application.
Thermowell: A closed-end tube designed to protect
temperature sensors from harsh environments, high
pressure, and flows. They can be installed into a system
by pipe thread or welded flange and are usually made
of corrosion-resistant metal or ceramic material
depending upon the application.
Transducer: A device which converts the parameter
being measured into another form which is its output.
For example, a thermocouple transforms heat into a
millivolt output.
Transducer: A device which converts the parameter
being measured into another form which is its output.
For example, a thermocouple transforms heat into a
millivolt output.
Transmitter (two-wire): A device which is used to transmit
temperature data from either a thermocouple or RTD
via a two-wire current loop. The loop has an external
power supply and the transmitter acts as a variable
resistor with respect to its input signal.
Transmitter (two-wire): A device which is used to transmit
temperature data from either a thermocouple or RTD
via a two-wire current loop. The loop has an external
power supply and the transmitter acts as a variable
resistor with respect to its input signal.
Triac: A solid state switching device used to switch
alternating current wave forms.
Triac: A solid state switching device used to switch
alternating current wave forms.
Surge current: A current of short duration occurring when
power is initially applied to capacitive or resistive loads,
usually lasting no more than several cycles.
Surge current: A current of short duration occurring when
power is initially applied to capacitive or resistive loads,
usually lasting no more than several cycles.
Temperature gradient: The range of temperature variations
at various physical locations throughout a thermal
system.
Temperature gradient: The range of temperature variations
at various physical locations throughout a thermal
system.
Thermal system: A regulated environment consisting of a
heat source, heat transfer medium, sensing device and
a process variable control instrument.
Thermal system: A regulated environment consisting of a
heat source, heat transfer medium, sensing device and
a process variable control instrument.
Thermocouple break protection: Fail-safe operation that
assures output shutdown upon an open thermocouple
condition.
Thermocouple break protection: Fail-safe operation that
assures output shutdown upon an open thermocouple
condition.
Triple point (water): The thermodynamic state where all
three phases, solid, liquid, and gas may all be present
in equilibrium. The triple point of water is at .01 °C.
Triple point (water): The thermodynamic state where all
three phases, solid, liquid, and gas may all be present
in equilibrium. The triple point of water is at .01 °C.