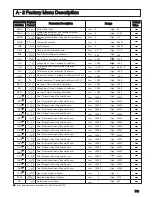
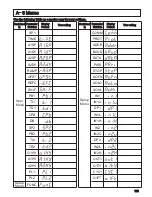
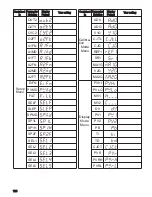
emf: Electromotive force. A rise in (electrical) potential
energy. The principal unit is the volt.
emf: Electromotive force. A rise in (electrical) potential
energy. The principal unit is the volt.
Electromagnetic interference (EMI): An electrical and
magnetic noise which can be generated when
switching inductive devices, lightning, radio wave
radiation, electrostatic discharge etc.
Electromagnetic interference (EMI): An electrical and
magnetic noise which can be generated when
switching inductive devices, lightning, radio wave
radiation, electrostatic discharge etc.
Emissivity: The ratio of energy emitted by an object to
the energy emitted by a blackbody at the same
temperature. The emissivity of an object depends
upon its material and surface texture; a polished metal
surface can have an emissivity around 0.2, and a
piece of wood can have an emissivity around 0.95.
Emissivity: The ratio of energy emitted by an object to
the energy emitted by a blackbody at the same
temperature. The emissivity of an object depends
upon its material and surface texture; a polished metal
surface can have an emissivity around 0.2, and a
piece of wood can have an emissivity around 0.95.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): A system meets
three requirements: 1. It does not cause interference
with other systems, 2. It is not susceptible to emissions
from other systems and 3. It does not cause
interference with itself.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): A system meets
three requirements: 1. It does not cause interference
with other systems, 2. It is not susceptible to emissions
from other systems and 3. It does not cause
interference with itself.
Event output: A programmable On/Off output used to
signal peripheral equipment or a process.
Event output: A programmable On/Off output used to
signal peripheral equipment or a process.
Exothermic: Gives off heat. A process is said to be
exothermic when it releases heat.
Exothermic: Gives off heat. A process is said to be
exothermic when it releases heat.
FM: Factory Mutual Research Corp. An organization
which sets industrial safety standards.
FM: Factory Mutual Research Corp. An organization
which sets industrial safety standards.
FM-approved: An instrument that meets a specific set of
specifications established by Factory Mutual Research
Corp.
FM-approved: An instrument that meets a specific set of
specifications established by Factory Mutual Research
Corp.
Flow rate: speed or velocity of fluid movement.
Flow rate: speed or velocity of fluid movement.
Fahrenheit: A temperature scale with 32 °F defined as the
ice point and 212 °F as the boiling point of water at sea
level.
Fahrenheit: A temperature scale with 32 °F defined as the
ice point and 212 °F as the boiling point of water at sea
level.
Event input: A programmable On/Off input used to signal
peripheral equipment or a process.
Event input: A programmable On/Off input used to signal
peripheral equipment or a process.
Error: The difference between the correct or desired
value and the actual reading or value taken.
Error: The difference between the correct or desired
value and the actual reading or value taken.
Endothermic: Absorbs heat. A process is said to be
endothermic when it absorbs heat.
Endothermic: Absorbs heat. A process is said to be
endothermic when it absorbs heat.
Filter: A low pass filter designed to minimize display
fluctuations.
Filter: A low pass filter designed to minimize display
fluctuations.
Form A: Single Pole Single Throw relay that only utilizes
the N.O. and common contacts. These contacts close
when the relay coil is energized. The contacts open
when power is removed from the control.
Form A: Single Pole Single Throw relay that only utilizes
the N.O. and common contacts. These contacts close
when the relay coil is energized. The contacts open
when power is removed from the control.
Form B: Single Pole Single Throw relay that only utilizes
the N.C. and common contacts. These contacts will
open when the relay coil is energized. The contacts will
close when power is removed from the control.
Form B: Single Pole Single Throw relay that only utilizes
the N.C. and common contacts. These contacts will
open when the relay coil is energized. The contacts will
close when power is removed from the control.
Form C: Single Pole Double Throw. Utilizes the N.O., N.C.
and common contacts. The user has the option of
wiring for a Form A or Form B contact. Refer to the Form
A and Form B above for more information.
Form C: Single Pole Double Throw. Utilizes the N.O., N.C.
and common contacts. The user has the option of
wiring for a Form A or Form B contact. Refer to the Form
A and Form B above for more information.
Heat of fusion: The amount of energy required to change
one pound of a material from a solid to a liquid without
an increase in temperature. Expressed in Btu/lb.
Heat of fusion: The amount of energy required to change
one pound of a material from a solid to a liquid without
an increase in temperature. Expressed in Btu/lb.
Heat of vaporization: The amount of energy required to
change one pound of a material from a liquid to a vapor
without an increase in temperature. Expressed in Btu/lb.
Heat of vaporization: The amount of energy required to
change one pound of a material from a liquid to a vapor
without an increase in temperature. Expressed in Btu/lb.
Heat sink: 1. Thermodynamic. A body which can absorb
thermal energy. 2 Practical. A finned piece of metal
used to dissipate the heat of solid state components
mounted on it.
Heat sink: 1. Thermodynamic. A body which can absorb
thermal energy. 2 Practical. A finned piece of metal
used to dissipate the heat of solid state components
mounted on it.
Heat transfer: The process of thermal energy flowing
from a body of high energy to a body of low energy.
Means of transfer are: Conduction, the two bodies in
contact; Convection, a form of conduction where the
two bodies in contact are of different phases, i.e; solid
and gas; Radiation, all bodies emit infrared radiation
Heat transfer: The process of thermal energy flowing
from a body of high energy to a body of low energy.
Means of transfer are: Conduction, the two bodies in
contact; Convection, a form of conduction where the
two bodies in contact are of different phases, i.e; solid
and gas; Radiation, all bodies emit infrared radiation
Heat treating: A process for treating metals where heating
to a specific temperature and cooling at a specific rate
changes the properties of the metal.
Heat treating: A process for treating metals where heating
to a specific temperature and cooling at a specific rate
changes the properties of the metal.
Hertz (Hz): Unit in which frequency is expressed.
Synonymous with cycles per second.
Hertz (Hz): Unit in which frequency is expressed.
Synonymous with cycles per second.
fpm: Flow velocity in feet per minute.
fpm: Flow velocity in feet per minute.
GIGA: The prefix for one billion (G).
GIGA: The prefix for one billion (G).
gph: The volumetric flow rate in gallons per hour.
gph: The volumetric flow rate in gallons per hour.
gpm: The volumetric flow rate in gallons per minute.
gpm: The volumetric flow rate in gallons per minute.
Grounded junction: A thermocouple junction in which the
sheath and conductors are welded together forming a
completely sealed integrated junction.
Grounded junction: A thermocouple junction in which the
sheath and conductors are welded together forming a
completely sealed integrated junction.
Heat: Thermal energy expressed in Calories, Btu's or
Joules.
Heat: Thermal energy expressed in Calories, Btu's or
Joules.
Gain: The amount of amplification used in an electrical
circuit.
Gain: The amount of amplification used in an electrical
circuit.
Freezing point: The temperature at which the substance
goes from the liquid phase to the solid phase.
Freezing point: The temperature at which the substance
goes from the liquid phase to the solid phase.
fps: Flow velocity in feet per second.
fps: Flow velocity in feet per second.
Frequency: The number or event occurrences or cycles
over a specified period of time.
Frequency: The number or event occurrences or cycles
over a specified period of time.
Fuse: A device that interrupts power in a circuit when an
overload occurs.
Fuse: A device that interrupts power in a circuit when an
overload occurs.
Fuzzy logic: An artificial intelligence technique that allows
control decisions to be made upon approximate or
incomplete information. Fuzzy logic is a continuous
decision making function that can prevent initial
overshoot and set point differentials.
Fuzzy logic: An artificial intelligence technique that allows
control decisions to be made upon approximate or
incomplete information. Fuzzy logic is a continuous
decision making function that can prevent initial
overshoot and set point differentials.
Ground: 1. The electrical neutral line having the same
potential as the surrounding earth. 2. The negative
side of dc power supply. 3. Reference point for an
electrical system.
Ground: 1. The electrical neutral line having the same
potential as the surrounding earth. 2. The negative
side of dc power supply. 3. Reference point for an
electrical system.
117