Chapter 5
RA83/84/85/93/94/95 Series
Basic Operation
Operation Manual
APPENDIX 1: Interpretation of Radar Images
F
actors that affect the radar detection range
93142105-02
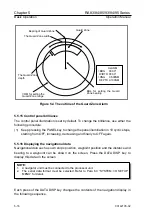
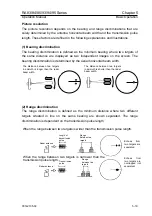
Radar Horizon
The radar uses microwave energy that
travels in a straight line like light. Light is
reflected towards the surface of the earth
due to the temperature, humidity, and the
atmospheric pressure changes in the air.
This causes the visual range to extend
beyond the physical horizon. This is called
the optical horizon. Microwave has the same
effect and this is called the radar horizon.
Meanwhile, its wavelength is longer than
that of light. The radar visual range is
therefore longer than light by approximately
6%.
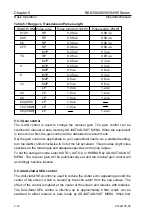
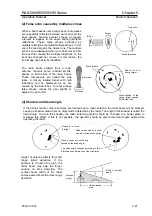
Sub-refraction
When cold air flows over a warm surface,
the microwave is bent upwards as shown in
the figure. This phenomenon is called
sub-refraction. As a result, the detectable
range may be reduced. This situation is
likely to occur in the Polar Regions, or in
warm current waters where cold air from the
Polar Regions flow over the sea surface.
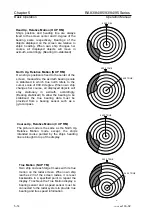
Super-refraction
When the air being warmed up in an inland
area flows over the cold sea, the microwave
is bent downwards. In this case, a
detectable radar range may increase. This
situation may occur produced in warm
coastal regions, and it becomes noticeable
as the temperature difference becomes
larger.
Ducting
When two or more layers of different
temperature come into contact with one
another, the radar wave may be reflected
from the boundary surface where different
refraction indices exist. As a result, the
microwave propagates along the curvature
of the earth while being reflected on the
wave passage situated between the
interface and the surface of the earth. This
passage is called “Duct”, and an abnormal
propagation of the radio wave caused by the
duct is called “Ducting”. If the air layers with
mutually different temperature or
atmospheric pressures are alternately
present along the different altitudes, radar
may be able to detect a target far beyond its
maximum detectable range.
H2
Antenna
D
Target
Earth
H1
Warm air
Antenna
Detectable range is shortened
Cold air
Warm air
Antenna
Detectable range is lengthened
Cold air
Earth
Antenna
Warm air
Cold air
Ducting
Warm air
Earth
Earth
Sub-refraction
Super-refraction
D=2.2(
√
H1 +
√
H2)
Radar Horizon
5-18