53
2.9
Application Notes
2.9.1
Notes on Data Access
1. Access to Empty Areas:
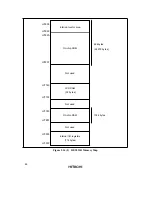
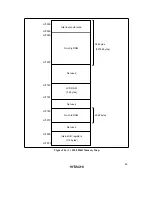
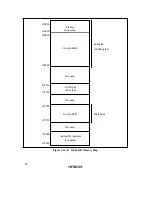
The address space of the H8/300L CPU includes empty areas in addition to the RAM,
registers, and ROM areas available to the user. If these empty areas are mistakenly accessed
by an application program, the following results will occur.
Data transfer from CPU to empty area:
The transferred data will be lost. This action may also cause the CPU to misoperate.
Data transfer from empty area to CPU:
Unpredictable data is transferred.
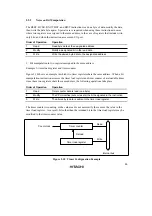
2. Access to Internal I/O Registers:
Internal data transfer to or from on-chip modules other than the ROM and RAM areas makes
use of an 8-bit data width. If word access is attempted to these areas, the following results will
occur.
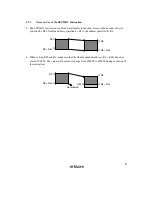
Word access from CPU to I/O register area:
Upper byte: Will be written to I/O register.
Lower byte: Transferred data will be lost.
Word access from I/O register to CPU:
Upper byte: Will be written to upper part of CPU register.
Lower byte: Unpredictable data will be written to lower part of CPU register.
Byte size instructions should therefore be used when transferring data to or from I/O registers
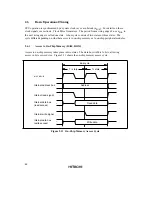
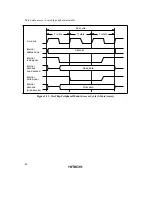
other than the on-chip ROM and RAM areas. Figure 2.17 shows the data size and number of
states in which on-chip peripheral modules can be accessed.