22
2.4.2
Effective Address Calculation
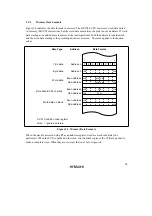
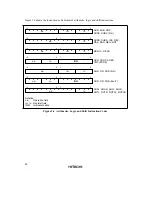
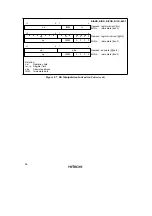
Table 2.2 shows how effective addresses are calculated in each of the addressing modes.
Arithmetic and logic instructions use register direct addressing (1). The ADD.B, ADDX, SUBX,
CMP.B, AND, OR, and XOR instructions can also use immediate addressing (6).
Data transfer instructions can use all addressing modes except program-counter relative (7) and
memory indirect (8).
Bit manipulation instructions can use register direct (1), register indirect (2), or 8-bit absolute
addressing (5) to specify the operand. Register indirect (1) (BSET, BCLR, BNOT, and BTST
instructions) or 3-bit immediate addressing (6) can be used independently to specify a bit position
in the operand.