63
11. PID control
■
◆PID control
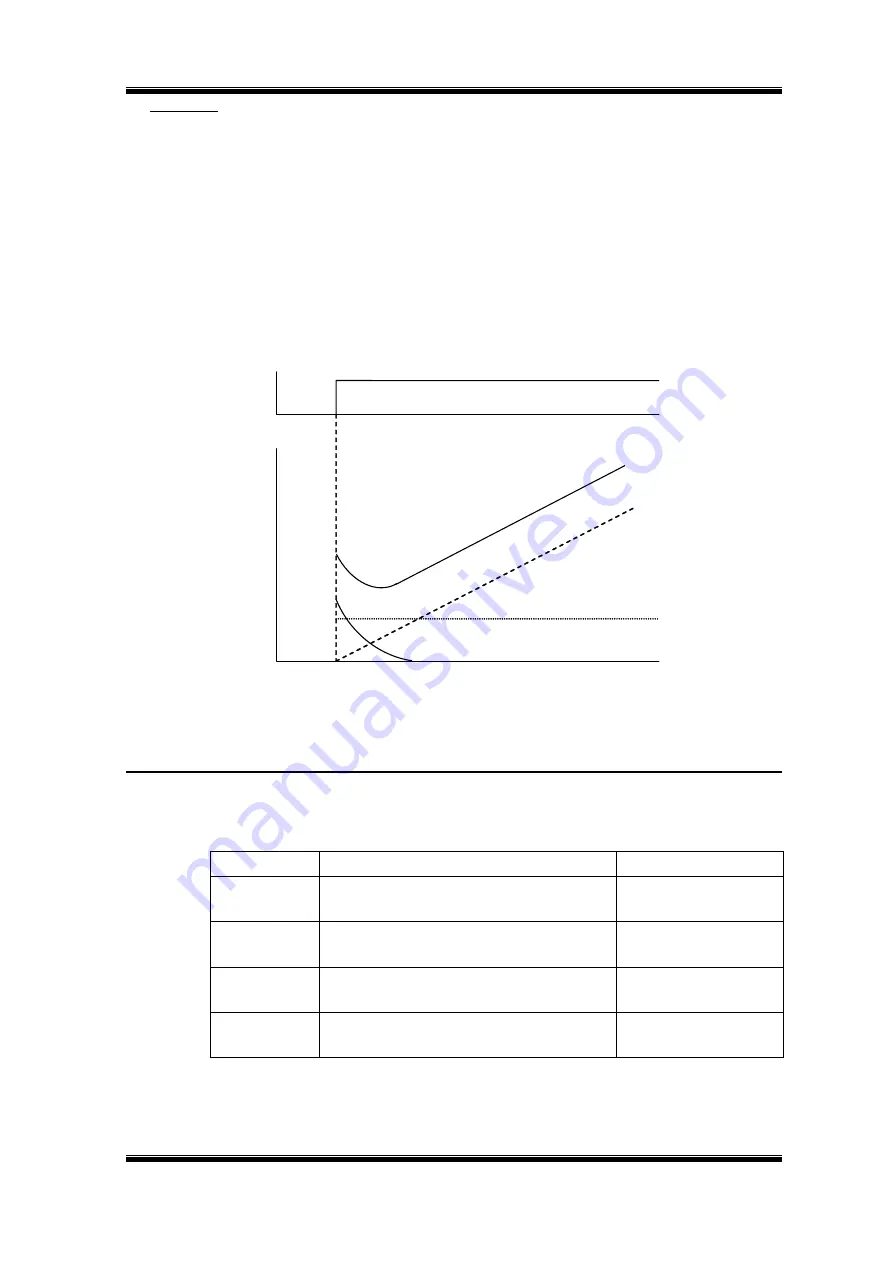
PID control is a method of making the feedback value match the set target value. By combinating proportional
control (P)、integral control (I) and derivative control (D), you can even control targets that you want to reach
status.
The characteristics of the PID control operations as below:
Proportional control (P): output of operation proportional to the error. Feedback value cannot equal to target
when only use Proportional control.
Integral control ( I ): output of operation integral to the error.Used for matching feedback value to target value,
however, intense change might cause intergral control to disperse.
Derivative control (D): output of operation derivative to the error, respond rapid variations.
PID
coutrol motion
■ PID control application
The following table shows example of PID control application usinginverter:
Application Control
details Example of sensor used
Speed control
Feeds back machinery speed information, and
matches speed to the target value.
Tachometer generator
Pressure control
Feeds back pressure information, and performs
constant pressure control.
Pressure sensor
Flow rate
control
Feeds back flow rate control information, and
controls the flow rate highly accurately.
Flow rate sensor
Temperature
control
Feeds back temperature information, and
performs temperature adjustment control.
Thermocouple thermistor
Output
Error
Time
P
coutrol
I
coutrol
D
PID
coutrol
coutrol






























