UG-707
ADV8005 Hardware Reference Manual
3.2.2.2.
Horizontal Down Scaler
Although the VOM has both horizontal and vertical scalers, there is also a horizontal down scaler in the VIM. The purpose of the VIM down
scaler is to save external memory bandwidth by doing horizontal downscaling before writing video data into the external memory to save
memory bandwidth.
The down scaler in the VIM should only be enabled when horizontal downscaling is needed, which means that the number of horizontal
output active pixels should be less than the number of horizontal input active pixels. When album mode is enabled, the specified active output
video width should be the album width.
If the horizontal resolution of the PVSP output timing is less than the input timing, the horizontal down scaler can be enabled to reduce the load
on the external DDR2 memory. This horizontal down scaler input resolution is defined by the
output resolution is defined by the
pvsp_vim_d_scal_out_width[10:0]
register. To enable the horizontal down scaler,
should be set to 1.
pvsp_vim_d_scal_enable
, Primary VSP Map,
Address 0xE883[5]
This bit is used to enable the VIM down scaler.
Function
pvsp_vim_d_scal_enable
Description
0 (default)
Disable VIM down scaler
1
Enable VIM down scaler
pvsp_vim_d_scal_out_width[10:0]
, Primary VSP Map,
Address 0xE83A[2:0]; Address 0xE83B[7:0]
This signal is used to set the output video width of the down-scaling scaler in the VIM. The input video width is set by register
pvsp_vim_crop_width. If VIM crop is not enabled, pvsp_vim_crop_width is auto configured by pvsp_autocfg_input_vid, which is the same
with input video's horizontal resolution.
Function
pvsp_vim_d_scal_out_width[
10:0]
Description
0x000 (default)
Default
0xXXX
Output width of VIM scalar
3.2.2.3.
Scaler Interpolation Mode
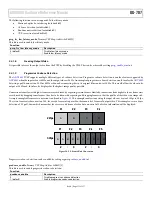
This section describes the method for scaling the input video data. The purpose of the scaler is to allow different input formats to be displayed
on a screen with a fixed resolution. The VIM scaler is usually used for downscaling, for example, 1080p to be downscaled to a lower definition
format such as 480p. Different scaling interpolation modes will affect scaler performance. The options for video scaling modes are described
below and are chosen using
Proprietary ADI Algorithm
This is a custom algorithm developed by ADI which allows improved performance in the scaling of the input video. This can reduce many
common artifacts when scaling video data such as:
•
Saw tooth
– otherwise known as ‘jaggies’, this is an artifact that occurs when an image is zoomed in and is one of the most important
criteria when evaluating scaling performance.
•
Edge blurring
– when zooming in, most high frequency information is lost, resulting in edges becoming blurred. The proprietary ADI
algorithm keeps the edge region sharp by retaining the high frequency information.
•
Ringing
– also known as the Gibbs phenomenon, can be found on video due to a reduction in high frequency information. The
proprietary ADI algorithm helps with the reduction of such artifacts.
Sharp/Smooth
Both the sharp/smooth options for scaler interpolation are versions of the proprietary ADI algorithm. The sharp and smooth versions allow for
limited customization of the scaler function. This function can be set depending on the user preference.
Bilinear
The bilinear option uses an averaging method within a 2x2 pixel array to increase the size of the input frame. This is a cruder method of scaling
than the default proprietary ADI Algorithm. In most cases, the scaler should be left at the default setting.
Rev. A | Page 116 of 317