UAG4100 User’s Guide
199
C
H A P T E R
1 9
ALG
19.1 ALG Overview
Application Layer Gateway (ALG) allows the following application to operate properly through the
UAG’s NAT.
• FTP - File Transfer Protocol - an Internet file transfer service.
The ALG feature is only needed for traffic that goes through the UAG’s NAT.
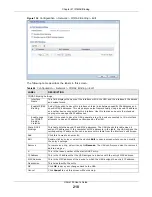
19.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
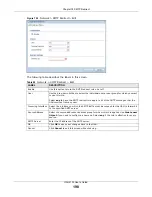
Use the
ALG
screen (
) to set up the FTP ALG settings.
19.1.2 What You Need to Know
Application Layer Gateway (ALG), NAT and Firewall
The UAG can function as an Application Layer Gateway (ALG) to allow certain NAT un-friendly
applications to operate properly through the UAG’s NAT and firewall. The UAG dynamically creates
an implicit NAT session and firewall session for the application’s traffic from the WAN to the LAN.
The ALG on the UAG supports all of the UAG’s NAT mapping types.
FTP ALG
The FTP ALG allows TCP packets with a specified port destination to pass through. If the FTP server
is located on the LAN, you must also configure NAT (port forwarding) and firewall rules if you want
to allow access to the server from the WAN.
ALG and Trunks
If you send your ALG-managed traffic through an interface trunk and all of the interfaces are set to
active, you can configure routing policies to specify which interface the ALG-managed traffic uses.
You could also have a trunk with one interface set to active and a second interface set to passive.
The UAG does not automatically change ALG-managed connections to the second (passive)
interface when the active interface’s connection goes down. When the active interface’s connection
fails, the client needs to re-initialize the connection through the second interface (that was set to
passive) in order to have the connection go through the second interface.