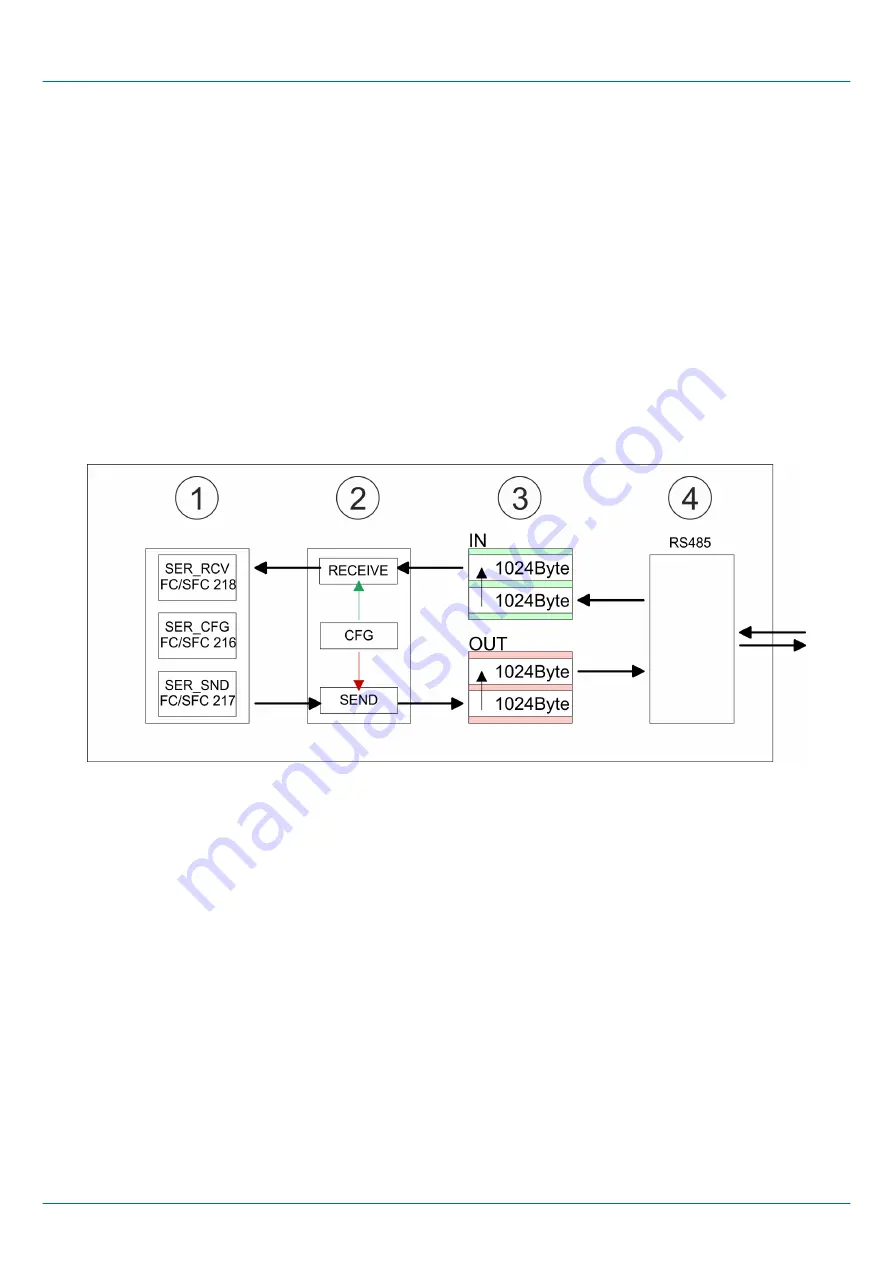
7.2 Principle of the data transfer
The data transfer is handled during runtime by using FC/SFCs. The principle of data
transfer is the same for all protocols and is shortly illustrated in the following.
n
Data, which are written into the according data channel by the CPU, is stored in a
FIFO send buffer (first in first out) with a size of 2x1024byte and then put out via the
interface.
n
When the interface receives data, this is stored in a FIFO receive buffer with a size of
2x1024byte and can there be read by the CPU.
n
If the data is transferred via a protocol, the embedding of the data to the according
protocol happens automatically.
n
In opposite to ASCII and STX/ETX, the protocols 3964R, USS and Modbus require
the acknowledgement of the partner.
n
An additional call of the FC/SFC 217 SER_SND causes a return value in RetVal that
includes among others recent information about the acknowledgement of the partner.
n
Further on for USS and Modbus after a SER_SND the acknowledgement telegram
must be evaluated by a call of the FC/SFC 218 SER_RCV.
1
Program
2
Protocol
3
FIFO buffer
4
Interface
7.3 Deployment of RS485 interface for PtP
Per default, the RS485 interface is deactivated. Via hardware configuration the RS485
interfaces may be switched to PtP operation (
p
oint
t
o
p
oint) via the parameter
Function
RS485
of the
Properties.
Since the VIPA specific CPU parameters may be set, the installation of the
SPEEDBUS.GSD from VIPA in the hardware catalog is necessary. The CPU may be con-
figured in a PROFIBUS master system and the appropriate parameters may be set after
installation.
RS485 PtP communication
Activate RS485 to PtP
operation
Requirements
VIPA System 300S
+
Deployment PtP communication
Deployment of RS485 interface for PtP
HB140 | CPU | 314-6CF23 | en | 19-01
138















































