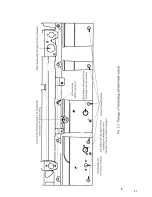
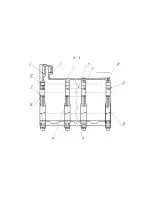
28
.7 General technical requirements for inspection of the components and assembly
units
2.7.1 During repair (current
o
r main) of the engine reasons for replacement of damaged,
worn or defected parts for the proper ones (from the parts) can be the result of inspection and
maximum allowable parameters of the inspected parts according to the present documents (in the
inspection sheets).
2.7.2 Change of the service properties of the engine while operation is connected with the
mechanical, heating and chemical influence leading to the wear, structural changes, change of the
physical and chemical properties of the materials. As a result of the irreversible processes in the
design defects and damages appear which lead to the more intensive serious wear and malfunction of
the parts and engine in general.
The main defects that occur are:
- change of the sizes, geometric form of the working surfaces as a result of wear;
- degradation of accuracy of the relative relation of the working surfaces on the detail;
- mechanical damages (cracks, gaps, breakage, flows like bending, coiling, buckling);
- fatigue break-down;
- corrosive damage;
- change of the physical and chemical properties of the details;
2.7.3 Analysis of the technical condition, reasons of the appearance of the damages and
defects of the parts is necessary to make a decision in order to prevent their occurrence, to increase
the running time of the engine, to decrease the idle time of the vehicle.
2.7.4 After the disassembling all parts and assembly units coming for the inspection should
be properly cleaned from the operational impurities, washed and dried. It is necessary for objective
estimation of the technical condition during the inspection.
2.7.5 During the inspection to decrease labour intensity it is useful to check at first those
defects according to which the part or assembly unit should be rejected (cracks in the critical
sections, cracks at the finished surfaces and other defects according to the inspection sheets).
2.7.6 To defect the parts by the measurements one should begin with those surfaces which
determine the operation time, are worn, exceed the allowed limits and should be rejected due to the
lack of ability of effective recovery, for example, measuring the piston one should measure at first
the groove for the upper compression ring, measuring the cylinder block one should measure the
Summary of Contents for ???-236
Page 25: ...26...
Page 26: ...27 2...
Page 40: ......
Page 41: ......
Page 53: ......
Page 56: ......
Page 59: ......
Page 64: ...236 238 1003014 3 236 238 1003014 4 236 238 1003014...
Page 65: ......
Page 70: ......
Page 73: ......
Page 81: ......
Page 85: ......
Page 92: ......
Page 95: ......
Page 101: ......
Page 113: ......
Page 119: ......
Page 122: ......
Page 125: ......
Page 128: ......
Page 142: ......
Page 144: ......
Page 150: ......
Page 155: ......
Page 158: ......
Page 160: ......
Page 165: ......
Page 193: ...N u M a r Method defect detection and Dimension and parameter mm...
Page 201: ...4 Thread stripping M16 1 5 6H no more than two threads Inspection To calibrate the thread...