Symbolic Manipulation
259
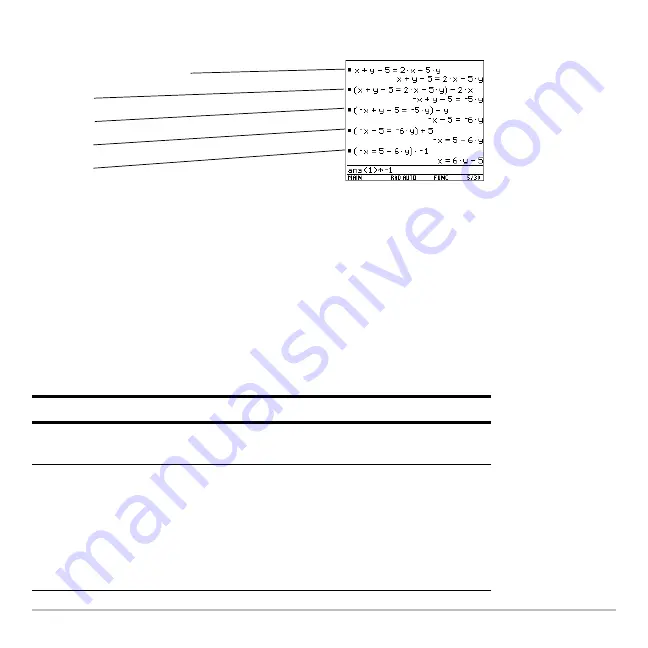
To see intermediate results, you can manually solve the equation step-by-step.
Note:
An operation such as
|
2
p
subtracts 2x from both sides.
Solving a System of Linear Equations
Solving a System of Linear Equations
Solving a System of Linear Equations
Solving a System of Linear Equations
To solve this system of equations, use any of the following methods.
Consider a set of two equations with two
unknowns:
2x
N
3y = 4
L
x + 7y =
L
12
Method
Example
Use the
solve
function for a one-step
solution.
solve(
2x
N
3y=4 and
L
x+7y=
L
12,{x,y}
)
Use the
solve
function with
substitution ( | ) for step-by-step
manipulation.
Substitutions are in the form of an
equality, such as x=3 or y=sin(x). To
be most effective, the left side should
be a simple variable.
See ”Symbolic Manipulation” in the
Previews
chapter, which solved for
x =
L
8/11
and
y =
L
20/11
.
x
«
y
|
5
Á
2x
|
5y
|
2 x
|
y
«
5
p
?
1
Summary of Contents for Voyage 200
Page 36: ...Getting Started 36 D B D B Press Result ...
Page 45: ...Getting Started 45 3 0 D B D D B D Press Result ...
Page 46: ...Getting Started 46 D 2 0 0 2 D B Scroll down to October and press Press Result ...
Page 60: ...Getting Started 60 B D Press Result ...
Page 139: ...Previews 139 8 Complete the operation Press 2 d Steps and keystrokes Display 5 f 2 ...
Page 453: ...Differential Equation Graphing 453 ...
Page 468: ...Tables 468 ...
Page 777: ...Activities 777 ...
















































