Functions, monitoring, and protective functions
9.3 Extended functions
Converter cabinet units
Operating Instructions, 07/2016, A5E03347396A
569
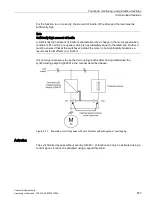
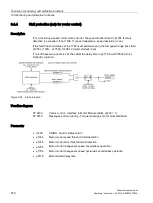
Calculating the load torque
The load torque must first be determined to determine the moment of inertia.
Figure 9-24 Calculating the load torque
Phases with constant speed not equal to zero are required to determine the load torque (e.g.
friction force).
For small speed changes, the converter calculates the load torque M
L
from the actual motor
torque.
The following conditions must be satisfied to do this:
●
Speed
≥ p1226
●
Acceleration setpoint < 8 1/s
2
●
Acceleration x moment of inertia (r1493) < 0.9 × p1560
Once the load torque is specified, the moment of inertia in the acceleration or deceleration
phase can be determined. If the source of p1502 has a 1 signal, the moment of inertia is not
estimated.
The accuracy of the moment of inertia estimation increases as the acceleration rate
increases. The start value of the moment of inertia estimator is the parameterized moment of
inertia (p0341 x p0342 + p1498).
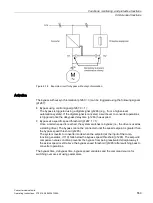
Calculating the moment of inertia
For larger changes, the converter initially calculates the accelerating torque M
B
as difference
between the motor torque M
M
, load torque M
L
and frictional torque M
R
:
M
B
= M
M
- M
L
- M
R
Summary of Contents for SINAMICS G150
Page 1: ......
Page 2: ......
Page 8: ...Foreword Converter cabinet units 8 Operating Instructions 07 2016 A5E03347396A ...
Page 18: ...Table of contents Converter cabinet units 18 Operating Instructions 07 2016 A5E03347396A ...
Page 679: ......
Page 680: ......