OEM6 Family Installation and Operation User Manual Rev 7
135
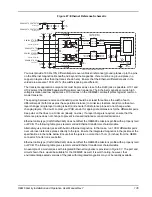
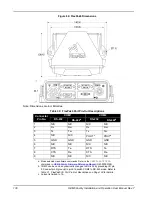
Figure 67: Ethernet Reference Schematic
You must provide 100
Ω
±10% differential pairs over unbroken reference (ground) planes up to the pins
on the Ethernet magnetics. Beneath and beyond the magnetics, there must be no ground plane (no
copper on layers other than the traces shown here). Ensure that the Ethernet differential pairs in the
voided area are also 100
Ω
±10% (the widths/spacing are different).
The transient suppression components must be placed as close to the RJ45 jack as possible. U101 and
U102 protect the OEM628 against differential mode transients. The Ethernet magnetics provide high
voltage isolation and low capacitance TVS devices on the OEM628 card itself protect against common
mode transients.
The spacing between receive and transmit pairs should be at least three times the width of each
differential pair (both traces plus the separation distance) to minimize crosstalk. Avoid more than two
layer changes (single layer routing is best) and ensure that reference planes do not change when
changing layers. If in doubt, contact your PCB vendor for appropriate dimensions for the differential pairs.
Keep vias on the lines to a minimum (ideally, no vias). If a layer change is required, ensure that the
reference plane does not change to prevent increased radiated or conducted emissions.
Ethernet cable type (Cat5/Cat5e/Cat6) does not affect the OEM628 emissions profile with a properly laid
out PCB. The following table gives recommended Ethernet transformer characteristics.
Alternately, use modular jacks with built-in Ethernet magnetics. In that case, run 100
Ω
differential pairs
over unbroken reference planes directly to the jack. Ensure the integrated magnetics in the jack meet the
specifications in the table below. Ensure that the jack is no more than 15 cm (6 inches) from the OEM6
connector. Shorter runs are better.
Ethernet cable type (Cat5/Cat5e/Cat6) does not affect the OEM628 emissions profile with a properly laid
out PCB. The following table gives recommended Ethernet transformer characteristics.
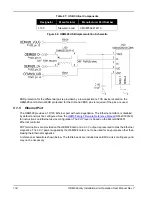
An example of a modular jack with integrated Ethernet magnetics is provided in
. The part and
circuit shown there would be suitable for the OEM628 as well. It is worth noting, however, that
environmentally-sealed versions of the jack with integrated magnetics may not be readily available.
R101
49.9-1%
R103
52.3-1%
R102
52.3-1%
R100
49.9-1%
Transient Suppression
(near RJ45 connector)
C106 1000 pF
1206 2kV
1206 2kV
SHELL1 SHELL2
MODULAR JACK
C105 1000pF
1206 2kV
ETH_TD-
ETH_RD-
U100
HALO TG110-E050N5RL
C100
0.1μF
C101
0.1μF
C102
0.01μF
C103
0.1μF
C104
0.1μF
C108
1000pF
1206 2kV
All planes voided beneath these traces!
C107
1000pF
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
FB100
FB101
DIFF PAIR (100 ohm)
DIFF PAIR (100 ohm)
DIFF PAIR
(100 ohm)
DIFF PAIR
(100 ohm)
DIFF PAIR
(100 ohm)
DIFF PAIR
(100 ohm)
FB102
ETH_3V3
ETH_3V3
ETH_3V3
P1502, pin 3
OEM628_ETH_CENTRETAP
P1502, pin 6
OEM628_ETH_CENTRETAP
P1502, pin 4
OEM628
P1502, pin 5
OEM628_ETH_TD-
P1502, pin 2
OEM628
P1502, pin 1
OEM628_ETH_RD-
U101
PLC03-6
IO1
GND1
GND2
IO2
IO4
GND4
GND3
IO3
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
TX+
TX-
RX+
NC1
NC2
RX-
NC3
NC4
9
10
11
T1_N
T1_CT
T1_P
U102
PLC03-6
IO1
GND1
GND2
IO2
IO4
GND4
GND3
IO3
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
14
15
16
T2_N
T2_CT
T2_P
12
13
5
4
NC1
NC2
T1_PS1
T1_CTS
T1_PS2
T2_PS1
T2_CTS
T2_PS2
NC3
NC4
8
7
6
3
2
1