CHAPTER 17 SERIAL INTERFACE IIC0 (
µ
PD780344Y, 780354Y SUBSERIES ONLY)
344
User’s Manual U15798EJ2V0UD
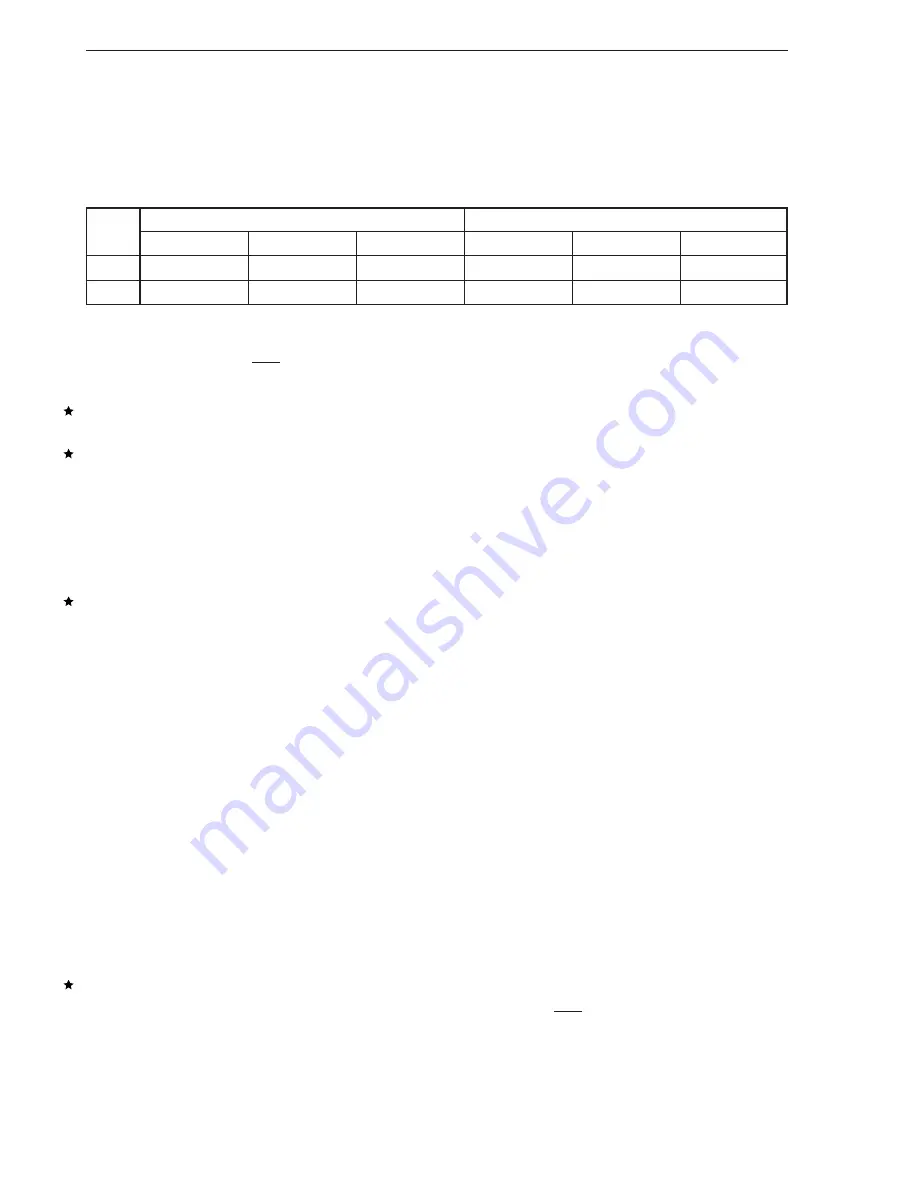
17.5.8 Interrupt request (INTIIC0) generation timing and wait control
The setting of bit 3 (WTIM0) of IIC control register 0 (IICC0) determines the timing by which INTIIC0 is generated
and the corresponding wait control, as shown in Table 17-2.
Table 17-2. INTIIC0 Timing and Wait Control
WTIM
During Slave Device Operation
During Master Device Operation
Address
Data Reception
Data Transmission
Address
Data Reception
Data Transmission
0
9
Notes 1, 2
8
Note 2
8
Note 2
9
8
8
1
9
Notes 1, 2
9
Note 2
9
Note 2
9
9
9
Notes 1.
The slave device’s INTIIC0 signal and wait period occurs at the falling edge of the ninth clock only when
there is a match with the address set to slave address register 0 (SVA0).
At this point, ACK is output regardless of the value set to IICC0’s bit 2 (ACKE0). For a slave device
that has received an extension code, INTIIC0 occurs at the falling edge of the eighth clock.
However, if an address mismatch is detected after a restart, INTIIC0 occurs at the falling edge of the
ninth clock, but a wait period is not generated.
2.
If the received address does not match the contents of slave address register 0 (SVA0) and an extension
code has not received, neither INTIIC0 nor a wait occurs.
Remark
The numbers in the table indicate the number of the serial clock’s clock signals. Interrupt requests and
wait control are both synchronized with the falling edge of these clock signals.
(1) During address transmission/reception
• Slave device operation:
According to the above
Notes 1
and
2
, the interrupt and wait timing are determined
regardless of the WTIM0 bit.
• Master device operation: The interrupt and wait timing occur at the falling edge of the ninth clock regardless
of the WTIM0 bit.
(2) During data reception
• Master/slave device operation: The interrupt and wait timing are determined according to the WTIM0 bit.
(3) During data transmission
• Master/slave device operation: The interrupt and wait timing are determined according to the WTIM0 bit.
(4) Wait cancellation method
The four wait cancellation methods are as follows.
• By setting bit 5 (WREL0) of IIC control register 0 (IICC0) to 1
• By writing to IIC shift register 0 (IIC0)
• By setting a start condition (setting bit 1 (STT0) of IICC0 to 1)
Note
• By setting a stop condition (setting bit 0 (SPT0) of IICC0 to 1)
Note
Note
Master only
When 8-clock wait has been selected (WTIM0 = 0), the output level of ACK must be determined prior to wait
cancellation.
(5) Stop condition detection
INTIIC0 is generated when a stop condition is detected.















































