25-20
MCF5282 User’s Manual
MOTOROLA
Programmer’s Model
interrupt routine can be fixed at compilation time. Each of the buffers is assigned a bit in
the IFLAG register. The bit is set when the corresponding buffer completes a successful
transmission or reception, and cleared when the CPU reads the interrupt flag register
(IFLAG) while the associated bit is set, and then writes it back as ‘1’ (and no new event of
the same type occurs between the read and the write actions).
The other 3 interrupt sources (Bus-off, Error and Wake-up) act in the same way, and are
located in the Error & Status register. The Bus-off and Error interrupt mask bits are located
in the CANCTRL0 register, and the Wake-up interrupt mask bit is located in the CANMCR.
25.5 Programmer’s Model
This section describes the registers in the FlexCAN module.
NOTE
The FlexCAN has no hard-wired protection against invalid
bit/field programming within its registers. Specifically, no
protection is provided if the programming does not meet CAN
protocol requirements.
Programming the FlexCAN control registers is typically done during system initialization,
prior to the FlexCAN becoming synchronized with the CAN bus. The configuration
registers can be changed after synchronization by halting the FlexCAN module. This is
done when the user sets the HALT bit in the FlexCAN module configuration register
(CANMCR). The FlexCAN responds by setting the CANMCR[NOTRDY] bit.
Additionally, the control registers can be modified while the MCU is in background debug
mode.
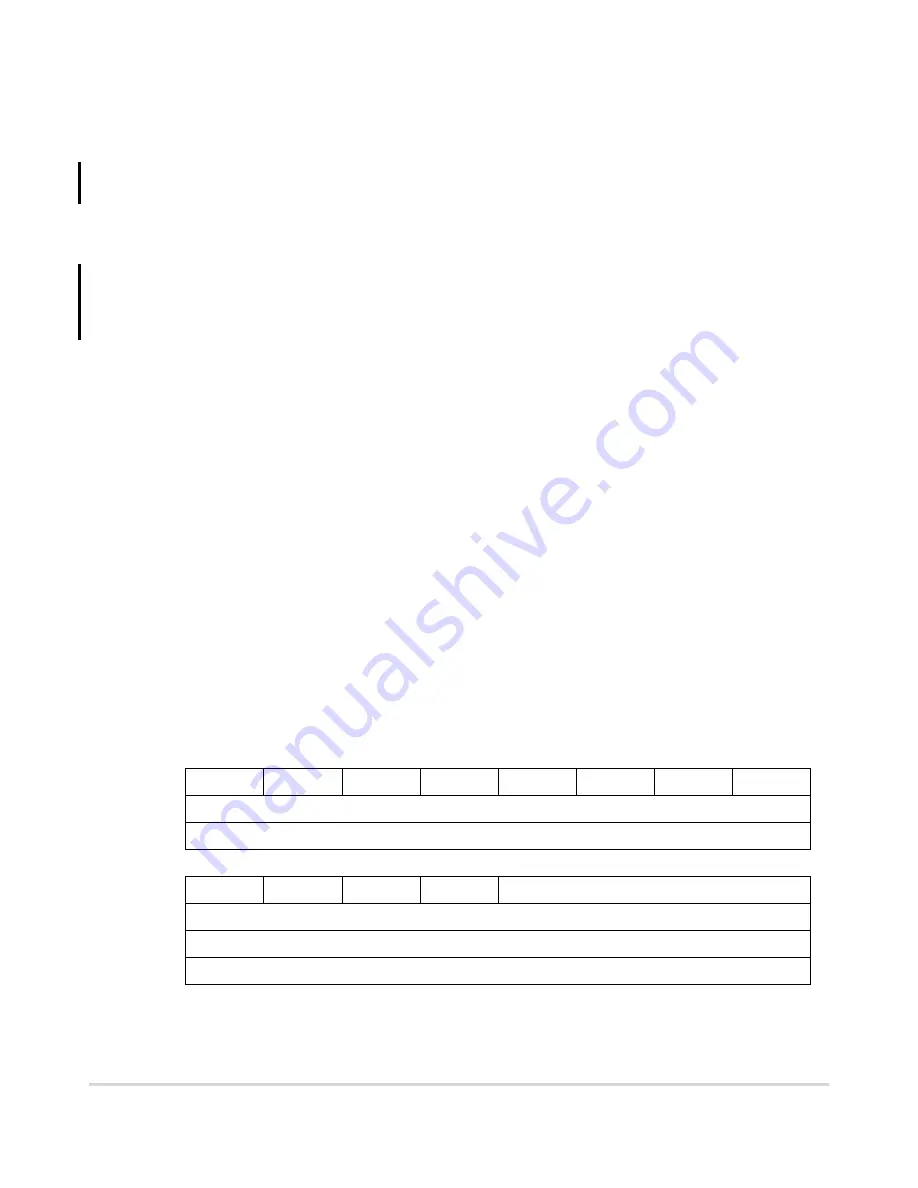
25.5.1 CAN Module Configuration Register (CANMCR)
Table 25-8 describes the CANMCR fields.
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
Field
STOP
FRZ
—
HALT
NOTRDY
WAKEMSK SOFTRST
FRZACK
Reset
0101_1001
R/W
R/W
7
6
5
4
3
0
Field
SUPV
SELFWAKE
APS
STOPACK
—
Reset
1000_0000
R/W
R/W
Address
0x1C_0000
Figure 25-6. CAN Module Configuration Register (CANMCR)
Summary of Contents for ColdFire MCF5281
Page 124: ...3 20 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA EMAC Instruction Set Summary ...
Page 141: ...MOTOROLA Chapter 5 Static RAM SRAM 5 5 SRAM Programming Model ...
Page 142: ...5 6 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA SRAM Programming Model ...
Page 168: ...6 26 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA Interrupts ...
Page 186: ...7 18 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA Functional Description ...
Page 228: ...9 22 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA Functional Description ...
Page 246: ...10 18 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA Low Power Wakeup Operation ...
Page 254: ...11 8 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA Memory Map and Registers ...
Page 264: ...12 10 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA Chip Select Registers ...
Page 280: ...13 16 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA Misaligned Operands ...
Page 314: ...14 34 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA MCF5282 External Signals ...
Page 339: ...MOTOROLA Chapter 15 Synchronous DRAM Controller Module 15 25 SDRAM Example ...
Page 340: ...15 26 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA SDRAM Example ...
Page 356: ...16 16 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA DMA Controller Module Functional Description ...
Page 408: ...17 52 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA Buffer Descriptors ...
Page 446: ...20 24 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA Interrupts ...
Page 474: ...22 18 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA Programming Model ...
Page 510: ...23 36 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA Operation ...
Page 526: ...24 16 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA I2C Programming Examples ...
Page 672: ...28 12 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA Functional Description ...
Page 718: ...29 46 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA Motorola Recommended BDM Pinout ...
Page 750: ...32 8 MCF5282 User s Manual MOTOROLA Ordering Information ...
















































