MI 2883 Energy Master
Theory and internal operation
136
P
lt
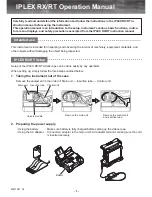
– 2 hours, long term flicker is calculated according to the following equation:
3
1
3
N
Pst
P
N
i
i
ltp
p: 1,2,3
(49)
5.1.10
Voltage and current unbalance
Standard compliance: IEC 61000-4-30 Class S (Section 5.7)
The supply voltage unbalance is evaluated using the method of symmetrical
components. In addition to the positive sequence component U
+
, under unbalanced
conditions there also exists negative sequence component U
-
and zero sequence
component U
0
. These quantities are calculated according to the following equations:
)
(
3
1
3
2
2
1
U
a
U
a
U
U
)
(
3
1
3
2
1
0
U
U
U
U
,
)
(
3
1
3
2
2
1
U
a
U
a
U
U
,
(50)
where
0
120
1
3
2
1
2
1
j
e
j
a
.
For unbalance calculus, instrument use the fundamental component of the voltage input
signals (U
1
, U
2
, U
3
), measured over a 10/12-cycle time interval.
The negative sequence ratio u
-
, expressed as a percentage, is evaluated by:
100
(%)
U
U
u
(51)
The zero sequence ratio u
0
, expressed as a percentage, is evaluated by:
100
(%)
0
0
U
U
u
(52)
Note:
In 3W systems zero sequence components U
0
and I
0
are by definition zero.
The supply current unbalance is evaluated in same fashion.
5.1.11
Underdeviation and overdeviation
Voltage Underdeviation
(U
Under
) and Overdeviation
(U
Over
) measurement method:
Standard compliance: IEC 61000-4-30 Class A (Section 5.12)
Basic measurement for the Underdeviation and Overdeviation is RMS voltage
magnitude measured over a 10/12-cycle time interval. Each RMS voltage
magnitude (i)
obtained through recording campaign is compared to nominal voltage U
Nom
from which
we express two vectors according to the formulas below:
Nom
RMS
Nom
Nom
RMS
i
RMS
i
Under
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
)
12
/
10
(
)
12
/
10
(
),
12
/
10
(
,
if
if
(53)