8400 motec | Software Manual
Motor control (MCTRL)
Braking operation/braking energy management
112
L
Firmware
≤
02.00 - DMS 2.1 EN - 03/2011
5.11
Braking operation/braking energy management
When electric motors are braked, the kinetic energy of the drive train is fed back into the
DC circuit regeneratively. This energy leads to an increase in the DC bus voltage. In order to
avoid overvoltage in the DC bus, several different strategies can be used:
Use of a brake resistor
Stopping of the deceleration when the brake chopper threshold is exceeded (HlgStop)
Use of the "inverter motor brake" function
(from version 02.00.00)
Overmagnetising the motor
(from version 02.00.00)
Combination of the above named options
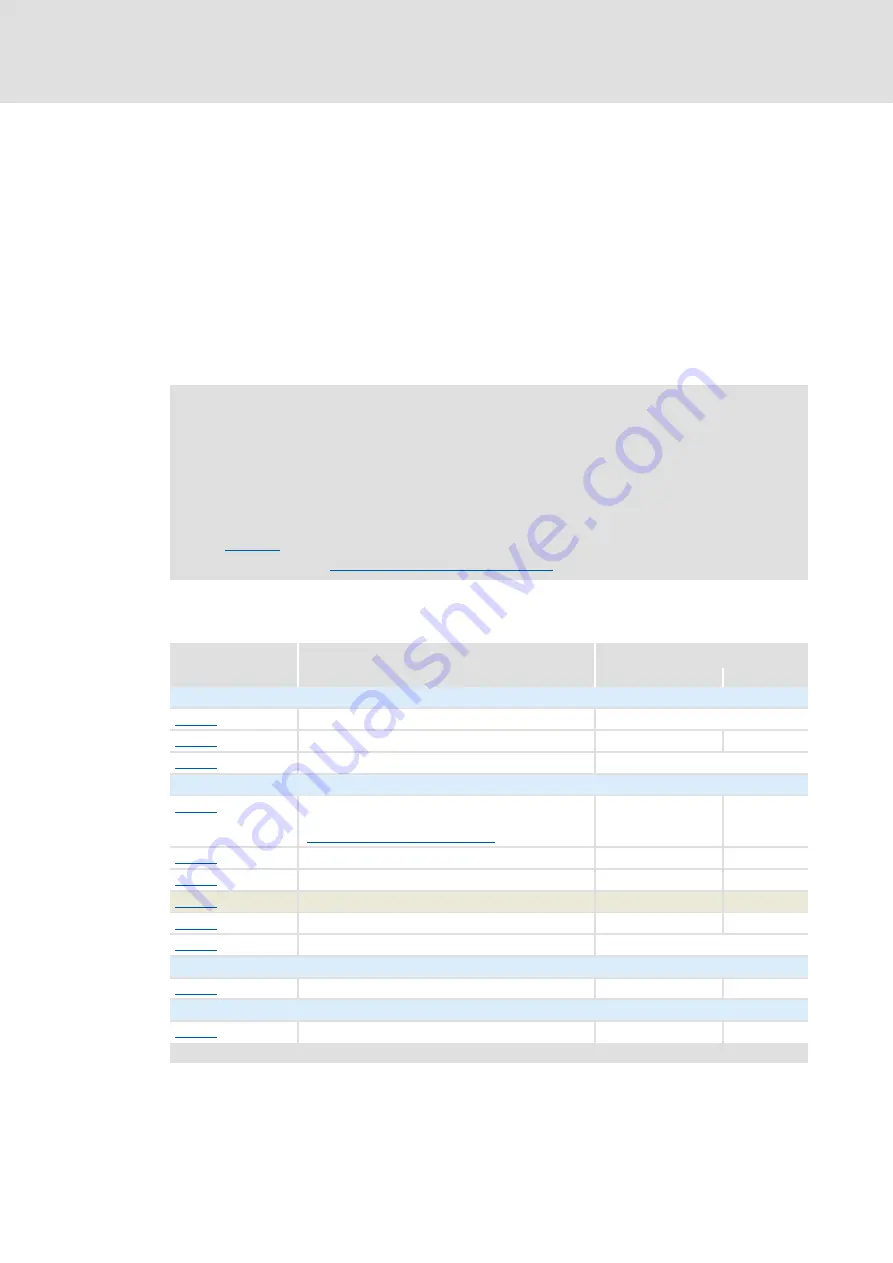
Short overview of the relevant parameters:
Stop!
If the connected brake resistor
• has a lower brake resistance value than the required brake resistor, the brake
chopper may be destroyed!
• has a too low thermal power dissipation, the brake resistor may be destroyed!
serves to parameterise the error response of the brake resistor
Brake resistor monitoring (I2xt)
Parameter
Info
Lenze setting
Value Unit
Basic settings
Mains voltage
3ph 400 V
Reduced brake chopper threshold
0 V
Reaktion brake resistor control
Brake resistor
Brake resistor
Value brake resistor
(dependent on the device power, see subchapter
"
Settings for internal brake resistor
")
220.0 Ohm
Rated power brake resistor
15 W
Heat capacity brake resistor
0.3 kWs
Brake resistor utilisation
- %
Brake resistor overload threshold
100 %
Response to brake resistor overtemperature
Fault
Inverter motor brake (variant 1)
Inverter motor brake: nAdd
80 rpm
Inverter motor brake (variant 2)
Inverter motor brake: Motor flux Add
20.0 %
Highlighted in grey = display parameter
Summary of Contents for 8400 motec Series
Page 375: ...L 375 ...






























