S
SCSI. Small computer system interface.
segment. A section of cable between components or
devices. A segment may consist of a single patch
cable, several patch cables that are connected, or a
combination of building cable and patch cables that are
connected.
serial port. An access point through which a computer
transmits or receives data, one bit at a time. Contrast
with parallel port.
server. (1) A functional unit that provides shared
services to workstations over a network. (2) In a
network, a data station that provides facilities to other
stations.
SIMM. Single-inline memory module.
slot. (1) A position in a device used for removable
storage media. (2) One of several receptacles in the
rear panel of the system unit into which a user can
install an adapter.
small computer system interface (SCSI). A standard
input/output interface used by personal computers.
SMP. symmetric multiprocessing.
socket. A receptacle for a microchip.
software. (1) All or part of the programs, procedures,
rules, and associated documentation of a computer.
Software is an intellectual creation that is independent
of the medium on which it is recorded. (2) Contrast
with hardware.
startup sequence. In personal computers, the order
that the computer uses to search the direct access
storage devices for an operating system.
storage. A functional unit into which data can be
placed, in which it can be retained, and from which it
can be retrieved.
straight-through cable. A type of 10BASE-T cable in
which the transmit and receive data pairs are wired so
that each signal wire is terminated at the same pin
position at each end of the cable. A straight-through
cable is used to connect the 10BASE-T port on an
Ethernet controller to a 10BASE-T port on a repeater
that performs the crossover function.
subsystem. In computers, a secondary or subordinate
system, usually capable of operating independently of a
controlling system, and usually having a single purpose,
such as displaying video or reading from and writing to
hard disks. A subsystem can be integrated into the
system board or on an adapter.
SVGA. Super video graphics array.
symmetric multiprocessing. In personal-computer
systems, a multiprocessing design that enables two or
more microprocessors to run concurrently and work
independently, with each microprocessor capable of
performing any task.
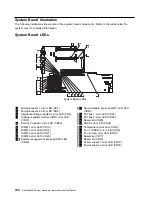
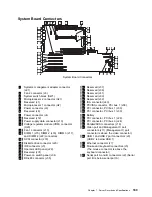
system board. In a system unit, the main circuit board
that supports a variety of basic system devices, such as
a keyboard or a mouse, and provides other basic
system functions.
T
token. In a local area network, the symbol of authority
passed successively from one data station to another to
indicate the station temporarily in control of the
transmission medium. Each data station has an
opportunity to acquire and use the token to control the
medium. A token is a particular message or bit pattern
that signifies permission to transmit.
transceiver. A physical device that connects a host
interface to a local area network, such as Ethernet.
Ethernet transceivers contain electronics that apply
signals to the cable and sense collisions.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). A
communications protocol used in Internet and in any
network that follows the U.S. Department of Defense
standards for inter-network protocol. TCP provides a
reliable host-to-host protocol between hosts in
packet-switched communications networks and in
interconnected systems of such networks. It assumes
that the Internet protocol is the underlying protocol.
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP). A set of protocols that allow cooperating
computers to share resources across a heterogeneous
network.
transmit. To send information from one place for
reception elsewhere. (A)
twisted pair. A transmission medium that consists of
two insulated electrical conductors twisted together to
reduce noise. (T)
182
Netfinity 5000 Server Hardware Information and Procedures