Troubleshooting 3-29
Soft Errors
This section provides information on Operating System (OS) soft errors that do not stop system operation.
The following list are the basic steps in troubleshooting the OS failures:
•
Determine the environment.
•
Check the error logs.
•
Run diagnostics.
•
Take appropriate action.
You must determine the environment. This means observing the front panel display and any console
messages. You should also check all error logs in the system and peripheral devices, if appropriate.
If needed, there are both offline and online diagnostics, as well as a system exerciser, that you can use to
troubleshoot the error. Once you determine the cause of the error, you can act accordingly.
Performance Problems
Another type of soft error is performance problems. A performance problem is characterized by unusually
slow response to one or more applications or user input. Some applications or user inputs may not get any
response. If the system seems to have a performance problem, use the recovery procedures in Table 3-16.
on page 3-29.
Diagnostic Tools
MPE/iX or HP-UX prior to 10.20 IPR 9707
Online Diagnostics
The online diagnostics require a user license and have password protection against unauthorized use. When
you purchase a support license, you will get a password.
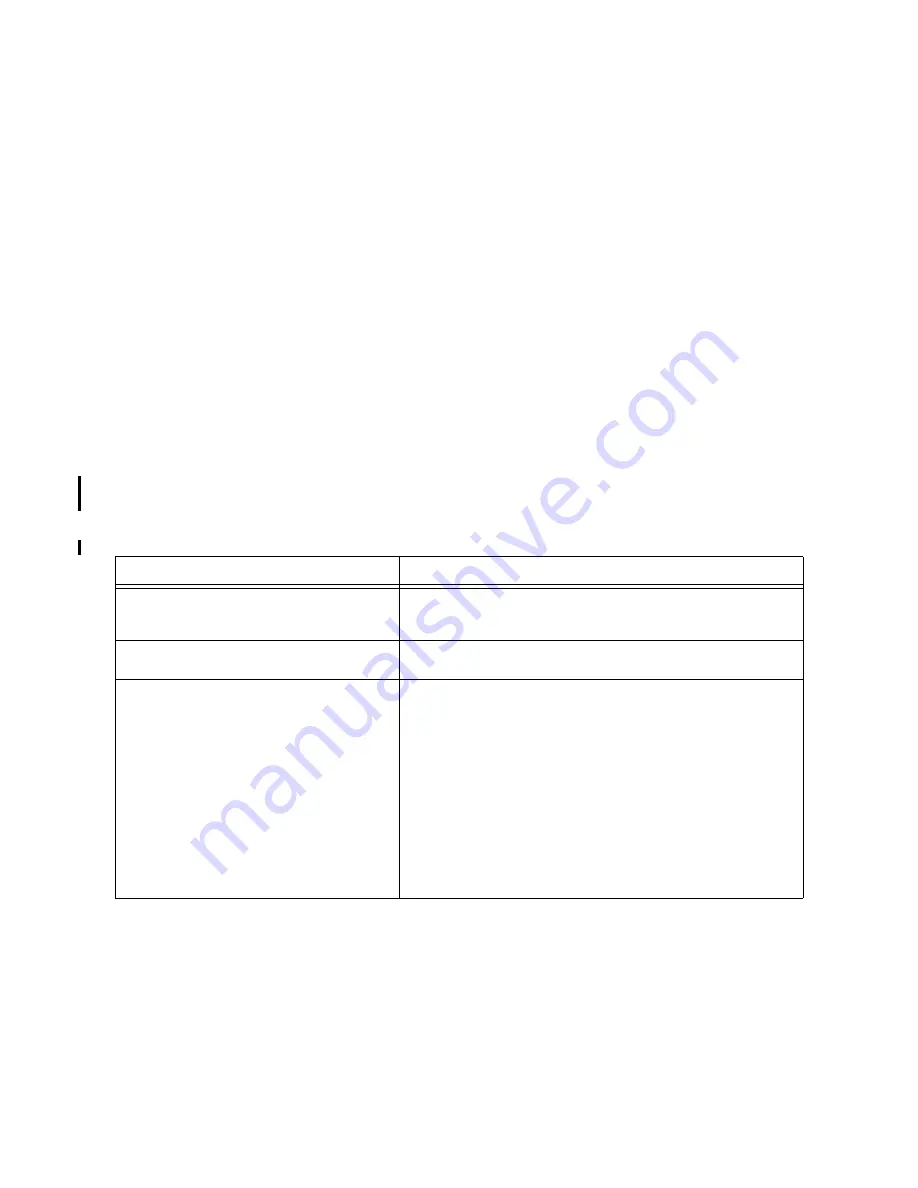
Table 3-16. System Performance Troubleshooting
Symptoms
Recovery Procedure
System responds slowly to one or more
programs/users.
See if any active processes are making heavy use of computer
resources. (For example, a massive compilation or a real time
process.)
Other programs/users cannot seem to get a
response.
Try sending an interrupt (Control-C) at a terminal.
System seems slow.
1. Check another terminal to verify that the problem is not just a
console hang.
2. Check the memory configuration for maximum performance,
especially if the memory has been recently upgraded.
3. Check CPU configuration with the
PR
command in the Infor-
mation menu.
4. Check for excessive I-Cache LPMCs in the system (refer to
Diagnostic Tools section).
5. Check IPRefetch configuration with the IPR command from
the Information or Configuration menu.
Summary of Contents for 3000/9x9KS Series
Page 14: ...xiv Contents E Sources of Information on the Web ...
Page 28: ...2 8 Install and Configuration Figure 2 4 HP PB I O Slot Location Diagram Kx70 Kx80 ...
Page 44: ...2 24 Install and Configuration ...
Page 68: ...3 24 Troubleshooting HP 3000 Core I O Figure 3 4 HP 3000 Core I O ...
Page 120: ...5 6 Diagnostics ...
Page 128: ...6 8 Replaceable Parts Figure 6 4 Peripheral Bay Expanded View ...
Page 136: ...6 16 Replaceable Parts ...
Page 150: ...7 14 Removal and Replacement Figure 7 11 Peripheral Bay Rear View ...
Page 180: ...7 44 Removal and Replacement Figure 7 35 Cabinet Exploded View Rear ...
Page 209: ...SCSI and I O 8 21 Figure 8 3 A3629A ST19171WD J2 and J6 Jumper Settings ...
Page 217: ...SCSI and I O 8 29 Figure 8 7 A3353A source 2 J3 Jumper Positions ...
Page 218: ...8 30 SCSI and I O Figure 8 8 A3353A source 2 Option Connector Jumper Positions ...
Page 280: ...8 92 SCSI and I O Diagnostics CSTM SCSIDDS SYSMAP IOMAP ...
Page 298: ...8 110 SCSI and I O Diagnostics SCSICD IOMAP SYSMAP ...
Page 302: ...8 114 SCSI and I O ...
Page 308: ...Support Information B 2 HP 9x9KS Block Diagram Figure B 1 HP 3000 9x9KS Block Diagram ...
Page 309: ...B 3 Support Information HP K100 Block Diagram Figure B 2 HP 9000 K100 Block Diagram ...
Page 310: ...Support Information B 4 HP K2x0 K4x0 Block Diagram Figure B 3 HP 9000 K2x0 K4x0 Block Diagram ...
Page 311: ...B 5 Support Information Kx70 Kx80 Block Diagram Figure B 4 HP9000 Kx70 Block Diagram ...
Page 342: ...Memory Configuration Guidelines C 16 ...
Page 350: ...D 8 New System Features ...
















































