iSXblue/SXBlue II GNSS Series Technical Reference Manual
145
8.
Troubleshooting
8.1
Troubleshooting Checklist
Use the following checklist to troubleshoot anomalous iSXBlue/SXBlue II GNSS system operation. The
following table provides a problem symptom, followed by a list of possible solutions.
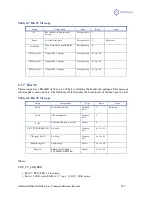
Table 8-1 Troubleshooting
Symptom
Possible Solution
Receiver fails to power
•
Recharge battery pack and try again after 15 minutes of charge
•
Verify contact modules between battery pack and receiver
•
Verify gasket around receiver’s battery contact module
No data or position from
iSXBlue/SXBlue II GNSS
•
Check receiver power status and/or battery pack
•
Verify that the receiver is configured to output data messages on the port you are communicating
with (you may issue a $JSHOW command with a terminal software to verify this)
•
Verify that iSXBlue/SXBlue II GNSS is locked to a valid DGPS signal (this can often be done on
the receiving device or with the use of HyperTerminal running on a PC)
•
Verify that iSXBlue/SXBlue II GNSS is locked to GPS satellites (this can often be done on the
receiving device or with the use of HyperTerminal running on a PC)
•
Check integrity and connectivity of data cable connections
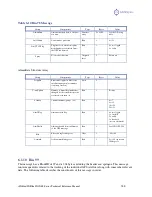
Random data from
iSXBlue/SXBlue II GNSS
•
Verify that the RTCM or Binary messages are not being output accidentally (send a $JSHOW
command to view the configuration of the receiver and the messages configured for output)
•
Verify that baud rate settings of iSXBlue/SXBlue II GNSS and remote device match correctly.
Bluetooth (PortA) must be set to 9600 baud on the receiver
•
Potentially, the volume of data requested to be output by the iSXBlue/SXBlue II GNSS could be
higher than the current baud rate supports. Try using a higher baud rate on the RS-232 and USB
ports.
No GPS lock
•
Check integrity of antenna cable
•
Verify antenna’s unobstructed view of the sky
•
Verify the lock status of GPS satellites (this can often be done on the receiving device or with the
use of HyperTerminal running on a PC)
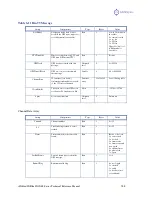
No SBAS lock
•
Check antenna connections
•
Verify antenna’s unobstructed view of the sky. If starting the receiver under dense forest canopy,
move the antenna location a bit until the DIFFerential LED (yellow) illuminates. See section
1.4.3.2 for field data collection guidelines
•
Verify the lock status of SBAS satellites (this can often be done on the receiving device or with the
use of HyperTerminal running on a PC – monitor BER value)
•
Verify that SBAS satellite PRN numbers being searched by the receiver are the proper ones
(WAAS, EGNOS, MSAS, GAGAN, etc). This may be verified with the $JWAASPRN command.
See Appendix C for a list of PRN numbers for the various active SBAS constellations
No DGPS position in external
RTCM mode
•
Verify that the baud rate of the RTCM input port matches the baud rate of the external source
•
Verify the pin-out between the RTCM source and the RTCM input port (transmit from the source
must go to receive of the RTCM input port and grounds must be connected - Refer to Appendix B)
Non-differential GPS output
•
Verify the SXBlue II GPS’ SBAS and lock status (or if external source is locked)
8.2
Using the LEDs to Troubleshoot
The iSXBlue/SXBlue II GPS receiver has 5 LED indicator lights that serve as status indicators. The first
4 lights should all be illuminated solid (non-blinking) when the receiver is powered on and has a valid
GPS and differential solution. The last LED (furthest to the right) should only be illuminated solid if you
are connected using Bluetooth communications. Otherwise, the lights can be in various states (blinking,
on solid, or off). Table 7-2 describes the LED lights operation.