ETEL Doc. - Operation & Software Manual # DSC2P 903 / Ver. F / 3/6/05
Chapter B: System setup & tuning
Operation & Software Manual
Direct Drives & Systems
49
8.3.4
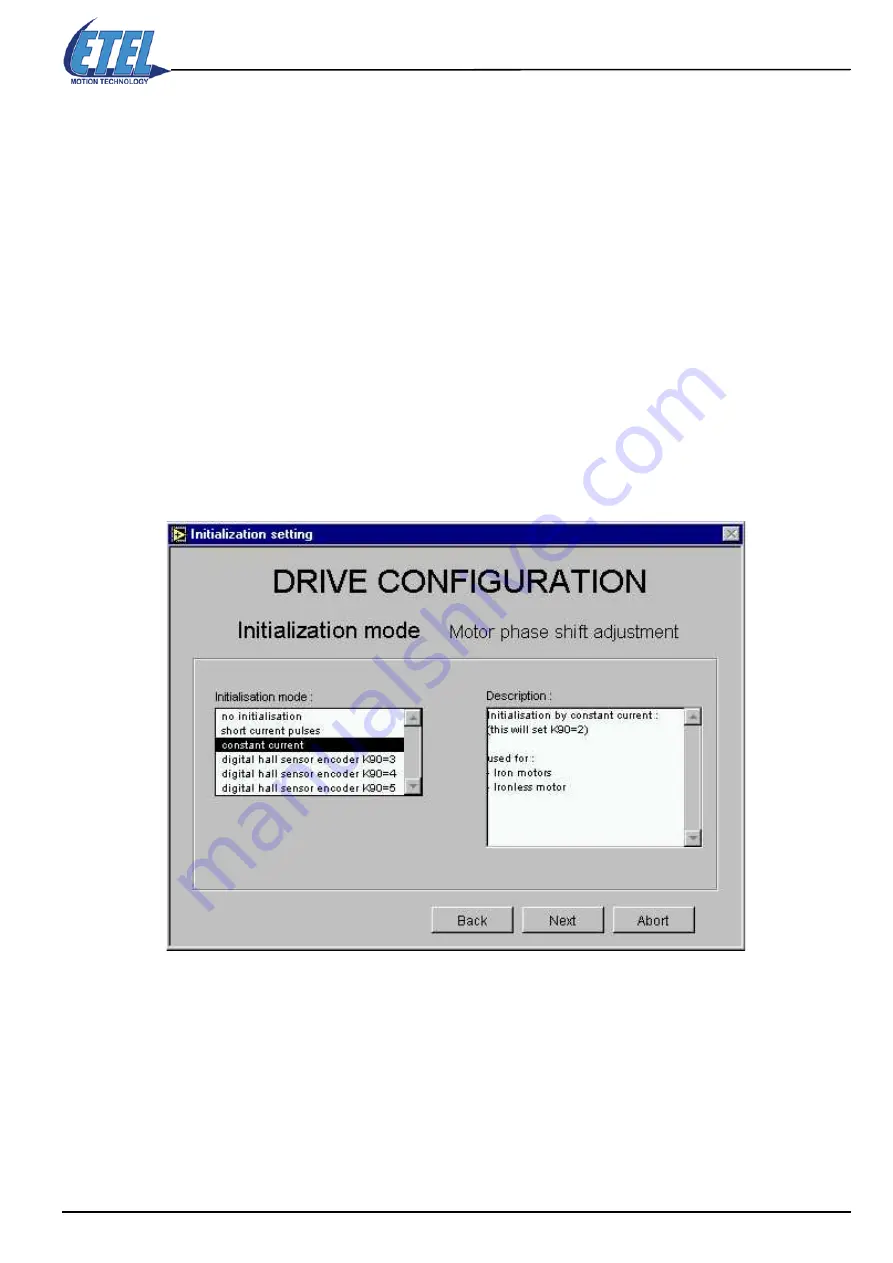
Initialization mode
There are two ways of initializing a motor:
The first consists in sending a
constant current
in the phases. In that case, the motor moves until it reaches
a 0 force position. Then, it stops on that
stable balance point
. Its position with respect to the magnets way
(motor's fixed part) is known because the stable balance point is always the same between two poles (as long
as the relation between the currents in the phases is constant). The longest stroke covered during the
initialization is equivalent to one magnetic period (32 mm for most ETEL's motors).
The 2
nd
way, which
only works with ironcore motors
, consists in sending
current pulses
to the motor
phases. It determines the motor position in relation with the magnets. The advantage of this method is that the
motor does not move, but it is not as precise as the first one (20% off the optimum phase shift adjustment).
This 2
nd
way should be especially used with vertical linear motors, or if the system mechanical friction is high.
After the initialization procedure, the motor position in relation with the magnets is known with a sufficient
accuracy to work out some movements. Sometimes, the accuracy may not be sufficient. The phase shift
adjustment quality may vary from an initialization to another depending on the initial position of the motor.
These problems will be solved with the
homing process
(refer to the next page).
The
constant current
mode is selected by default, this will always work for all motors with an encoder.
• If you are an experienced user, you may modify this default setting (refer to the explanations above).
• Click on the
NEXT
button and the next window will appear.






























