209
5. Parameter Description
Eaton Electric General Inverters DF1 Series
UMXXXXXXXXE February 2020 www.eaton.com
5.11.2 Zero-speed/zero-servo control
•
Zero-speed/ zero-servo function selection
Parameter
Name
Factory
Value
Setting Range
Content
10-03
P.151
Zero-speed control function
selection
0
0
There is no output at zero-speed.
1
The zero-speed running is carried out in close-loop vector
control (00-21/22=4) mode; DC voltage breaking is carried
out in V/F close-loop control (00-21/22=1) mode.
2
The zero-servo running is carried out in close-loop vector
mode.
10-04
P.152
Voltage at zero-speed control
4.0%
0~30.0%
7.5K/11KF and types below
2.0%
Types from 11K/15KF to 55K/75KF
1.0%
75K/90KF and types above
Zero-speed control
•
Make sure that 01-11 (start frequency) is set to zero when using this function.
ote:
N
1. Suppose that 10-04 = 6%, and then the output voltage of zero speed is 6% of base frequency voltage 01-04.
2. For V/F, V/F close-loop control, and close-loop vector control mode, please refer to the motor control mode parameter 00-21,
00-22.
Zeroservo
•
The zero servo function is a position loop that can keep the motor to stop at any position point (origin) and lock the
motor by external force at a certain position.
•
When zero servo is active, once the motor speed falls below the level set in parameter 10-00, the drive goes into
the zero servo mode and holds the current position. When the input assigned to trigger the Zero Servo function is
released and the run command is still present, the motor reaccelerates.
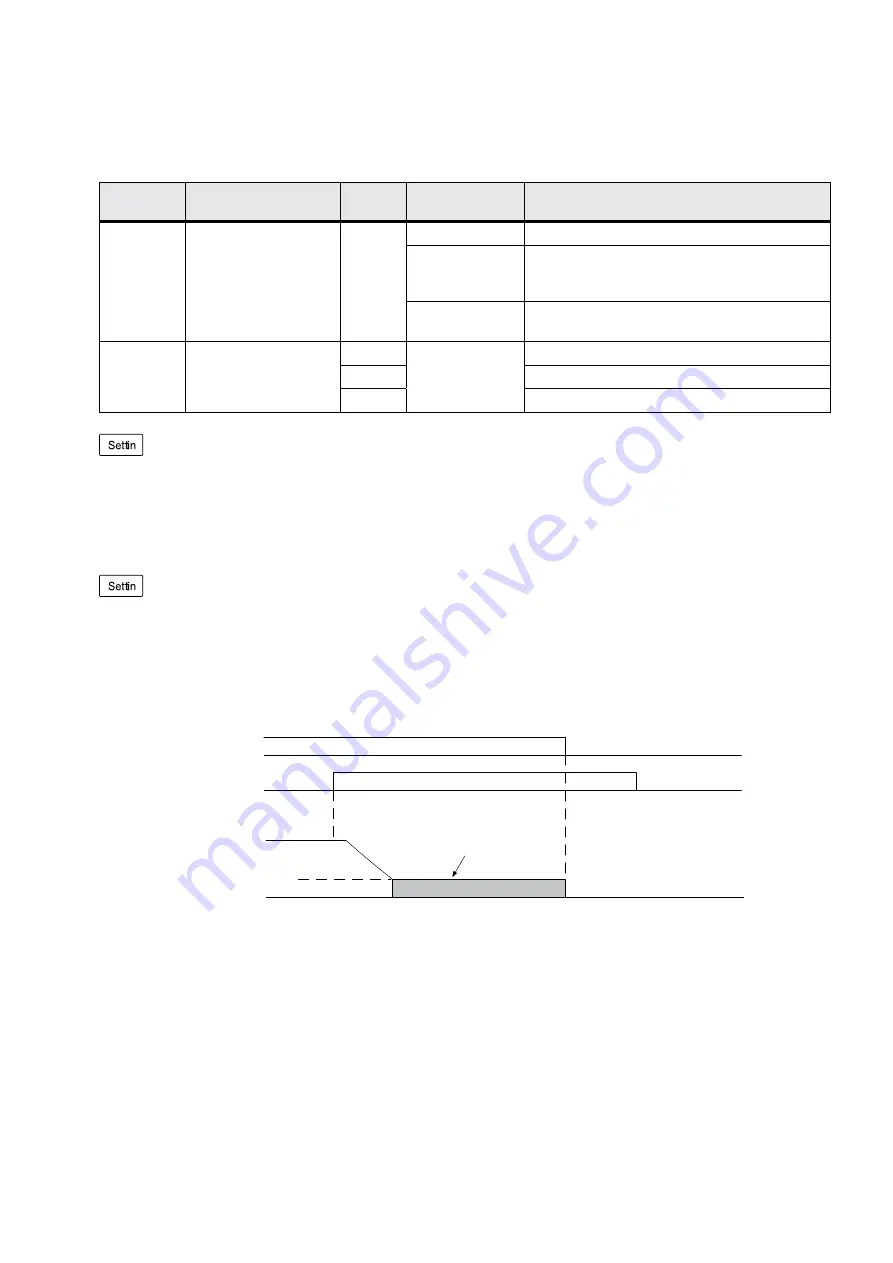
•
Zero servo operation:
ote:
N
Avoid using zero servo to lock 100% load for long periods, as this can trigger a fault. If such loads need to be held in place for
long periods, either make sure the current is less than 50% of the drive rated current during Zero Servo, or use a larger capacity
drive.
Run command
ON
Zero Servo
Operation
Zero servo
command
Motor speed
ON
OFF
OFF
P.10
(DC Injection Braking
start frequency)
















































