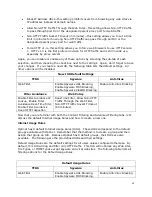
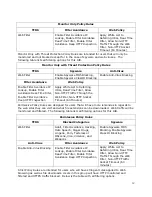
53
•
If you choose to enter a custom amount for the upload and download restrictions,
remember that this amount is presented in kilobits per second (Kbps). You will need
to compute your bandwidth into this amount (1024Kbps = 1 Mbps).
•
There are two application sets that you probably should not restrict: HTTP and
Uncategorized. The application set of HTTP correlates to all web-based traffic,
including regular web browsing. Because this application set is commonly used more
than any other application set, we recommend that you do not set a highly stringent
shaping rule for HTTP. The application set of Uncategorized correlates to network
traffic for which Optinet does not have an explicit signature. These applications
could be proprietary, recent, or uncommon. In addition to this, this application set
could also include traffic that is very important, such as a custom accounting
application, or an unrecognized VoIP system, etc. Because of this, we strongly
recommend that you do not disable this traffic or create a strict shaping rule for this
traffic.
•
Priority levels are only used when there is not enough bandwidth to complete
requests for active users or applications. For example, if you have two shaping
rules: 1Mbps for VPN with a High priority level and 1Mbps for P2P with a Low priority
level and there is not enough bandwidth to complete the requests for both
applications, Optinet will restrict P2P even more than 1Mbps to allocate more
bandwidth for VPN.
•
There can be some variance between shaping rules and reporting, especially with
P2P and Streaming Media, because of how initial communications for these
applications take place. For example, Bit Torrent will negotiate on random ports and
may be considered Uncategorized until data begins to pass. After data is passed
Optinet can identify Bit Torrent as P2P and will then report on all traffic passed
beginning with the initial connections. However, shaping rules for Bit Torrent will not
take effect until the data is confirmed as P2P, normally after the initial connections.
Below are some general expectations for the variance:
o
Shaping rules under 256K can have up to 20% difference in reporting
o
Shaping rules under 1M can have up to 10% difference in reporting
o
Shaping rules under 5M can have up to 5% difference in reporting
•
If you chose to shape a web URL, use general phrases. For instance, if you want to
shape traffic to the Web site YouTube, enter the phrase youtube instead of
http://www.youtube.com.
•
Web Content shaping rules take precedence over Application shaping rules and will
be recorded jointly for shared applications. For example, if you have an Application
shaping rule for Streaming Media at 1Mbps and a Web Content shaping rule for
YouTube at 1Mbps, the Web Content shaping rule will take preference while the
Application shaping rule will not apply. Reporting for the Streaming Media
Application Set will then report traffic for Streaming Media combined with traffic for
YouTube (2Mbps). To assure that Streaming Media does not exceed a specific
amount, balance the amount with Web Content shaping rules designated for
Streaming Media Web sites.
•
All changes to shaping rules will flush the Optinet forwarding plane. The forwarding
plane is the architecture that decides how to handle packets arriving on the LAN