P846/EN FD/D
Firmware Design
(FD) 9-16
MiCOM P846
I
p
mZr
(1m)Z
I
q
Zsq
Rf
I
f
Vp
Zsp
Eq
Ep
P0124ENa
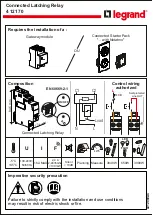
Figure 6: Two machine equivalent circuit
From this diagram:
Vp = m
Ι
pZr +
Ι
fRf
…(equation 1)
The fault location, m, can be found if
Ι
f can be estimated allowing equation 1 to be solved.
1.5.2
Data acquisition and buffer processing
The fault locator stores the sampled data within a 12 cycle cyclic buffer at a resolution of 32
samples per cycle. When the fault recorder is triggered the data in the buffer is frozen such
that the buffer contains 6 cycles of pre-trigger data and 6 cycles of post-trigger data. Fault
calculation commences shortly after this trigger point.
The trigger for the fault locator is user selectable via the programmable scheme logic.
The fault locator can store data for up to four faults. This ensures that fault location can be
calculated for all shots on a typical multiple re-close sequence.
FD
1.5.3
Faulted phase selection
Selection of the faulted phase(s) is performed by comparing the magnitude of the pre fault
and post fault values of the three phase-to-phase currents. A single phase-to-ground fault
produces the same change on two of these signals and zero on the third. A phase-to-phase
or double phase-to-ground fault produces one signal that is larger than the other two. A
three-phase fault produces the same change on all 3 currents.
Current changes are considered to be the same if they are within 20% of each other. Phase
selection and fault location calculation can only be made if the current change exceeds
5%
Ι
n.
1.5.4
The fault location calculation
This works by:
a)
First obtaining the vectors
b)
Selecting the faulted phase(s)
c)
Estimating the phase of the fault current,
Ι
f, for the faulted phase(s)
d)
Solving equation 1 for the fault location m at the instant of time where
Ι
f = 0
Summary of Contents for MiCOM P846
Page 2: ......
Page 4: ......
Page 5: ...Safety Section P846 EN SS H11 SS SAFETY SECTION...
Page 6: ...P846 EN SS H11 Safety Section SS...
Page 8: ...P846 EN SS H11 Safety Section SS 2 SS...
Page 16: ...P846 EN IT D Introduction MiCOM P846 IT...
Page 18: ...P846 EN IT D Introduction IT 1 2 MiCOM P846 IT...
Page 26: ...P846 EN TD D Technical Data MiCOM P846 TD...
Page 38: ...P846 EN GS D Getting Started MiCOM P846 GS...
Page 58: ...P846 EN ST D Getting Started MiCOM P846 ST...
Page 60: ...P846 EN ST D Settings ST 4 2 MiCOM P846 ST...
Page 78: ...P846 EN OP D Operation MiCOM P846 OP...
Page 104: ...P846 EN OP D Operation OP 5 26 MiCOM P846 OP...
Page 106: ...P846 EN AP D Application Notes MiCOM P846 AP...
Page 108: ...P846 EN AP D Application Notes AP 6 2 MiCOM P846 AP...
Page 122: ...P846 EN AP D Application Notes AP 6 16 MiCOM P846 AP...
Page 124: ...P846 EN PL D Programmable Logic MiCOM P846 PL...
Page 126: ...P846 EN PL D Programmable Logic PL 7 2 MiCOM P846 PL...
Page 144: ...P846 EN MR D Measurements and Recording MiCOM P846 MR...
Page 146: ...P846 EN MR D Measurements and Recording MR 8 2 MiCOM P846 MR...
Page 160: ...P846 EN FD D Firmware Design MiCOM P846 FD...
Page 182: ...P846 EN CM D Commissioning MiCOM P846 CM...
Page 228: ...P846 EN CM D Commissioning CM 10 46 MiCOM P846 CM...
Page 230: ...P846 EN MT D Maintenance MiCOM P846 MT...
Page 232: ...P846 EN MT D Maintenance MT 11 2 MiCOM P846 MT...
Page 238: ...P846 EN TS D Troubleshooting MiCOM P846 TS...
Page 240: ...P846 EN TS D Troubleshooting TS 12 2 MiCOM P846 TS...
Page 252: ...P846 EN SC D SCADA Communications MiCOM P846 SC...
Page 272: ...P846 EN SG D Symbols and Glossary MiCOM P846 SG...
Page 280: ...P846 EN SG D Symbols and Glossary SG 14 8 MiCOM P846 SG...
Page 282: ...P846 EN IN D Installation MiCOM P846 IN...
Page 284: ...P846 EN IN D Installation IN 15 2 MiCOM P846 IN...
Page 296: ...P846 EN IN D Installation IN 15 14 MiCOM P846 IN...
Page 297: ......