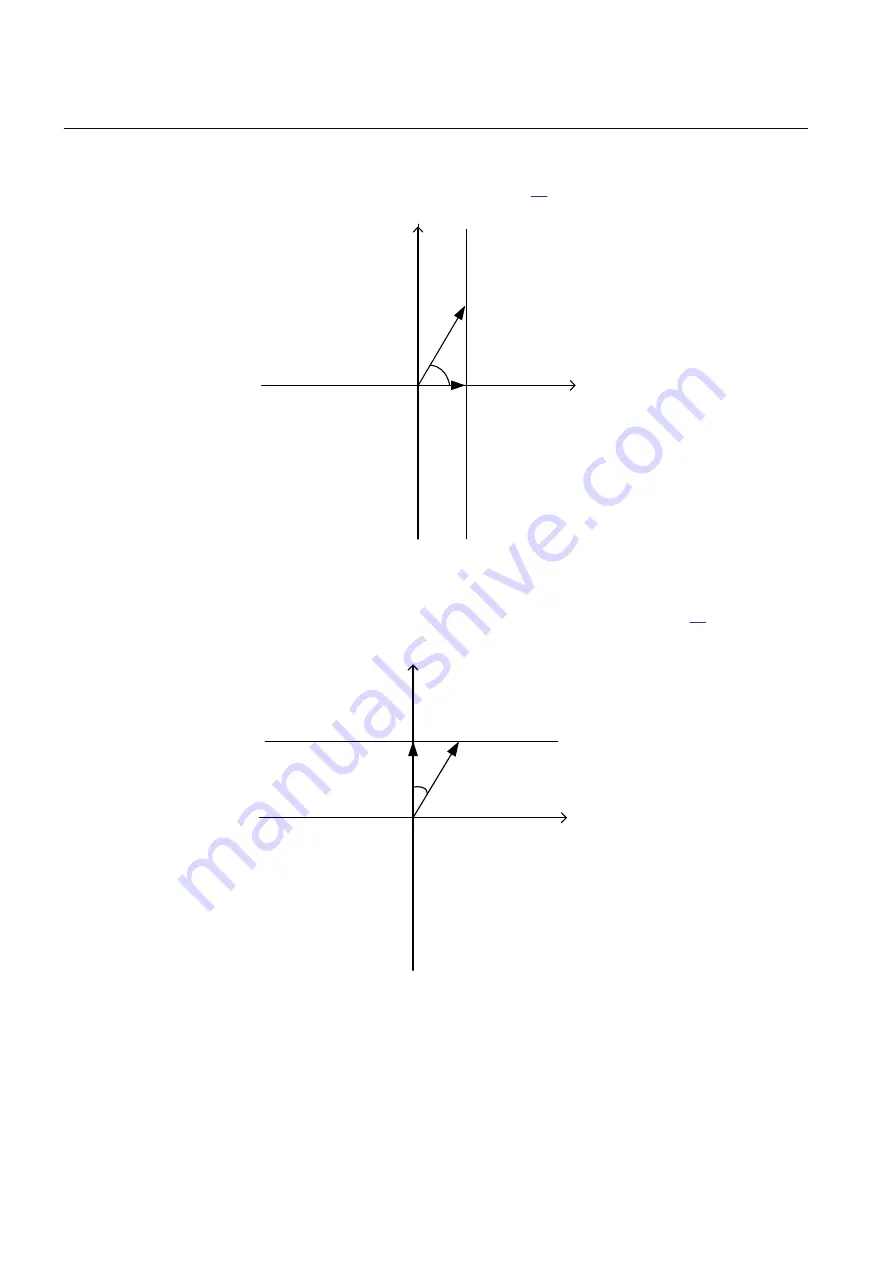
With
OpMode
set to
2I0cosfi
the current component in the direction equal to the
characteristic angle
RCADir
has the maximum sensitivity. The characteristic for
RCADir
is equal to 0° is shown in Figure
.
0 ,
90
RCADir
ROADir
0
2I
0
ref
ang(2I ) ang(2U
)
0
ref
2U
U
0
2I
cos
IEC16000127-1-en.vsdx
IEC16000127 V1 EN-US
Figure 59:
Characteristic for RCADir equal to 0°
The characteristic is for
RCADir
equal to -90° is shown in Figure
.
IEC16000128-1-en.vsdx
ref
U
90 ,
90
RCADir
ROADir
0
2
I
0
2
I
cos
0
(2 )
(
)
ref
ang
I
ang U
0
2
U
IEC16000128 V1 EN-US
Figure 60:
Characteristic for RCADir equal to -90°
When
OpMode
is set to
2U02I0cosfi
the apparent residual power component in the
direction is measured.
Section 8
1MRK 506 375-UEN A
Current protection
180
Railway application RER670 2.2 IEC
Application manual
Summary of Contents for RELION RER670
Page 1: ...RELION 670 SERIES Railway application RER670 Version 2 2 IEC Application manual ...
Page 2: ......
Page 22: ...16 ...
Page 48: ...42 ...
Page 70: ...64 ...
Page 80: ...74 ...
Page 100: ...94 ...
Page 210: ...204 ...
Page 364: ...358 ...
Page 384: ...378 ...
Page 468: ...462 ...
Page 494: ...488 ...
Page 504: ...498 ...
Page 505: ...499 ...
















































