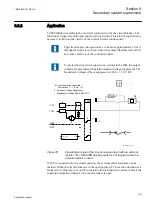
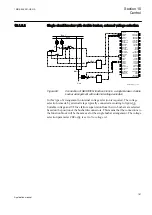
Several trip-circuit supervision functions parallel in circuit
Not only the trip circuit often have parallel trip contacts, it is also possible that the
circuit has multiple TCS circuits in parallel. Each TCS circuit causes its own
supervising current to flow through the monitored coil and the actual coil current is a
sum of all TCS currents. This must be taken into consideration when determining the
resistance of R
ext
.
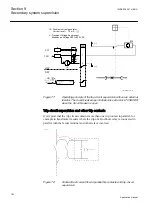
Trip-circuit supervision with auxiliary relays
Many retrofit projects are carried out partially, that is, the old electromechanical
relays are replaced with new ones but the circuit breaker is not replaced. This creates
a problem that the coil current of an old type circuit breaker can be too high for the
protection IED trip contact to break.
The circuit breaker coil current is normally cut by an internal contact of the circuit
breaker. In case of a circuit breaker failure, there is a risk that the protection IED trip
contact is destroyed since the contact is obliged to disconnect high level of
electromagnetic energy accumulated in the trip coil.
An auxiliary relay can be used between the protection IED trip contact and the circuit
breaker coil. This way the breaking capacity question is solved, but the TCS circuit in
the protection IED monitors the healthy auxiliary relay coil, not the circuit breaker
coil. The separate trip circuit supervision relay is applicable for this to supervise the
trip coil of the circuit breaker.
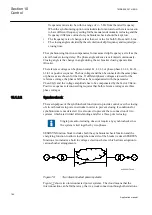
Dimensioning of the external resistor
Under normal operating conditions, the applied external voltage is divided between
the relay’s internal circuit and the external trip circuit so that at the minimum 20V
(3...20 V) remains over the relay’s internal circuit. Should the external circuit’s
resistance be too high or the internal circuit’s too low, for example due to welded relay
contacts, the fault is detected.
Mathematically, the operation condition can be expressed as:
(
)
20
C
ext
S
C
U
R
R
I
V DC
-
+
´
³
IECEQUATION16062 V1 EN
(Equation 78)
U
c
Operating voltage over the supervised trip circuit
I
c
Measuring current through the trip circuit, appr. 1.0 mA (0.85...1.20 mA)
R
ext
external shunt resistance
R
s
trip coil resistance
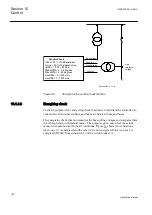
If the external shunt resistance is used, it has to be calculated not to interfere with the
functionality of the supervision or the trip coil. Too high a resistance causes too high
a voltage drop, jeopardizing the requirement of at least 20 V over the internal circuit,
while a resistance too low can enable false operations of the trip coil.
1MRK 505 291-UEN A
Section 9
Secondary system supervision
181
Application manual
Summary of Contents for Relion REQ650
Page 1: ...Relion 650 series Breaker protection REQ650 Application manual ...
Page 2: ......
Page 20: ...14 ...
Page 26: ...20 ...
Page 48: ...42 ...
Page 82: ...76 ...
Page 90: ...84 ...
Page 160: ...154 ...
Page 178: ...172 ...
Page 264: ...258 ...
Page 288: ...282 ...
Page 302: ...296 ...
Page 330: ...324 ...
Page 338: ...332 ...
Page 339: ...333 ...