User Manual
3onedata proprietary and confidential
Copyright © 3onedata Co., Ltd.
116
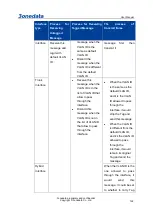
MAC Table Columns
Type
Indicates whether the entry is a static or a dynamic entry.
MAC Address
The MAC address of the entry.
VLAN
The VLAN ID of the entry.
Port Members
The ports that are members of the entry.
Buttons
Auto-refresh: Automatic refresh occurs every 3 seconds.
Refresh: Refreshes the displayed table starting from the "Start from MAC address" and
"VLAN" input fields.
Clear: refresh all dynamic entries.
: Updates the table starting from the first entry in the MAC Table, i.e. the entry
with the lowest VLAN ID and MAC address.
: Updates the table, starting with the entry after the last entry currently displayed.
6.2 VlAN
VLAN is Virtual Local Area Network. VLAN is the data switching technology that
logically (note: not physically) divides the LAN device into each network segment (or
smaller LAN) to achieve the virtual working group (unit).
VLAN advantages mainly include:
Port isolation. Ports in different VLAN, even in the same switch, can't
intercommunicate. Such a physical switch can be used as multiple logical
switches.
Network security. Different VLAN can't directly communicate with each other,
which has eradicated the insecurity of broadcast information.
Flexible management. Changing the network user belongs to needn't to change
ports or connection; only needs to change the firmware configuration.
That is, ports within the same VLAN can intercommunicate; otherwise, ports can't
communicate with each other. A VLAN is identified with VLAN ID, and ports with the
same VLAN ID belong to a same VLAN.